sEVs from tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through miR-486-5p
- PMID: 33348053
- PMCID: PMC8058446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.025
sEVs from tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through miR-486-5p
Abstract
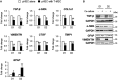
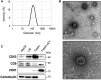
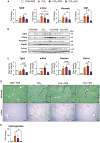
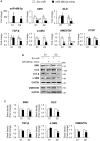
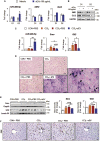
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are considered as a promising therapeutic tool for liver fibrosis, a main feature of chronic liver disease. Because small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) harboring a variety of proteins and RNAs are known to have similar functions with their derived cells, MSC-derived sEVs carry out the regenerative capacities of MSCs. Human tonsil-derived MSCs (T-MSCs) are reported as a novel source of MSCs, but their effects on liver fibrosis remain unclear. In the present study, we investigated the effects of T-MSC-derived sEVs on liver fibrosis. The expression of profibrotic genes decreased in human primary hepatic stellate cells (pHSCs) co-cultured with T-MSCs. Treatment of T-MSC-sEVs inactivated human and mouse pHSCs. Administration of T-MSC-sEVs ameliorated hepatic injuries and fibrosis in chronically damaged liver induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). miR-486-5p highly enriched in T-MSC-sEVs targeting the hedgehog receptor, smoothened (Smo), was upregulated, whereas Smo and Gli2, the hedgehog target gene, were downregulated in pHSCs and liver tissues treated with T-MSC-sEVs or miR-486-5p mimic, indicating that sEV-miR-486 inactivates HSCs by suppressing hedgehog signaling. Our results showed that T-MSCs attenuate HSC activation and liver fibrosis by delivering sEVs, and miR-486 in the sEVs inactivates hedgehog signaling, suggesting that T-MSCs and their sEVs are novel anti-fibrotic therapeutics for treating chronic liver disease.
Keywords: hepatic stellate cells; liver fibrosis; microRNA; small extracellular vesicles; tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Pinzani M., Rombouts K. Liver fibrosis: from the bench to clinical targets. Dig. Liver Dis. 2004;36:231–242. - PubMed
-
- Alhadlaq A., Mao J.J. Mesenchymal stem cells: isolation and therapeutics. Stem Cells Dev. 2004;13:436–448. - PubMed
-
- Alfaifi M., Eom Y.W., Newsome P.N., Baik S.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2018;68:1272–1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

