Increased levels of plasma cytokines and correlations to organ failure and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients
- PMID: 33348065
- PMCID: PMC7833204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155389
Increased levels of plasma cytokines and correlations to organ failure and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients
Abstract
Background: The infection caused by SARS CoV-2 has been postulated to induce a cytokine storm syndrome that results in organ failure and even death in a considerable number of patients. However, the inflammatory response in Corona virus disease-19 (Covid-19) and its potential to cause collateral organ damage has not been fully elucidated to date. This study aims to characterize the acute cytokine response in a cohort of critically ill Covid-19 patients.
Method: 24 adults with PCR-confirmed Covid-19 were included at time of admission to intensive care a median of eleven days after initial symptoms. Eleven adult patients admitted for elective abdominal surgery with preoperative plasma samples served as controls. All patients were included after informed consent was obtained. 27 cytokines were quantified in plasma. The expression of inflammatory mediators was then related to routine inflammatory markers, SAPS3, SOFA score, organ failure and 30-day mortality.
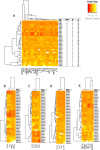
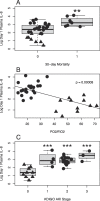
Results: A general increase in cytokine expression was observed in all Covid-19 patients. A strong correlation between respiratory failure and IL-1ra, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8 and IP-10 expression was observed. Acute kidney injury development correlated well with increased levels of IL-1ra, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17a, IP-10 and MCP-1. Generally, the cohort demonstrated weaker correlations between cytokine expression and 30-day mortality out of which IL-8 showed the strongest signal in terms of mortality.
Conclusion: The present study found that respiratory failure, acute kidney injury and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients are associated with moderate increases of a broad range of inflammatory mediators at time of admission.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Biomarkers; COVID-19; Cytokine storm; Inflammation; Intensive care.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

