Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33348220
- PMCID: PMC7723460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104715
Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The novel coronavirus pandemic is an ongoing challenge faced by the public and health care systems around the globe. Majority of information and evidence gathered so far regarding COVID-19 has been derived from data and studies in adult populations. Crucial information regarding the characterization, clinical symptomatology, sequelae, and overall outcomes in the pediatric population is lacking. As such, we aimed to conduct a comprehensive meta-analysis and systematic review to collect and analyze current evidence about COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
Method: A systematic search and review of scientific literatures was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines using PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Medline, and Google Scholar databases. All relevant studies until June 16, 2020 were included. Studies were reviewed for methodological quality, and random-effects model was used to conduct the primary meta-analysis. I2 value and Egger's test was used to estimate heterogeneity and publication bias respectively.
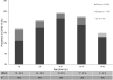
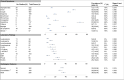
Results: We reviewed 20 eligible studies that included 1810 pediatric patient population (<21 yo) with PCR tested COVID-19 positivity. In pooled data, majority (25 % [CI 18-32], I2 59 %) of overall COVID-19 positive patients fell in the 6-10 yr age group. 13 % ([CI 11-14], I2 78 %) of the patients were asymptomatic, with headache (67 % [CI 60-74], I2 46 %), fever (55 % [CI 52-58], I2 61 %), and cough (45 % [CI 42-49], I2 79 %) accounting for the most prevalent physical signs seen in symptomatic patients. Leukopenia (12 % [CI 9-15], I250 %) and lymphopenia (15 % [CI 13-19], I2 85 %) was common. Elevated Ferritin (26 % [CI 16-40], I2 73 %), Procal (25 % [CI 21-29 %], I2 83 %), and CRP (19 % [CI 16-22 %], I2 74 %) were other laboratory abnormalities commonly observed. Common radiological features were ground-glass opacities (36 % [CI 32-39 %], I2 92 %), normal finding (33 % [CI 30-36 %], I2 81 %), and consolidation. 29 % ([CI 26-33], I2 85 %) of the patient cases was non-severe, whereas only 5 % ([CI 1-8], I2 87 %) was severe. Mortality was observed in 0.3 % ([CI 0.1-0.4], I2 0%) of the overall cases.
Conclusion: COVID-19 is prevalent across all pediatric age-groups and presents with varying degree of symptomology. However, children have a milder course of the disease with extremely favorable prognosis. Laboratory and radiological features are inconsistent and require further investigations. Additional studies are needed on this topic to corroborate findings and establish evidence-based and consistent characterization of COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical characteristics; Meta-analysis; Outcomes; Pediatric; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical features and outcomes of neonatal COVID-19: A systematic review.J Clin Virol. 2021 Jun;139:104819. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104819. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Clin Virol. 2021. PMID: 33862544 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- 2020. COVID-19 World Map and Mortality Analysis; p. 1.https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/mortality COVID-19. May 22, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

