The Regulation of Astrocytic Glutamate Transporters in Health and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33348528
- PMCID: PMC7766851
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249607
The Regulation of Astrocytic Glutamate Transporters in Health and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
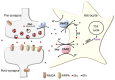
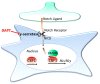
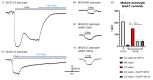
The astrocytic glutamate transporters excitatory amino acid transporters 1 and 2 (EAAT1 and EAAT2) play a key role in nervous system function to maintain extracellular glutamate levels at low levels. In physiology, this is essential for the rapid uptake of synaptically released glutamate, maintaining the temporal fidelity of synaptic transmission. However, EAAT1/2 hypo-expression or hypo-function are implicated in several disorders, including epilepsy and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as being observed naturally with aging. This not only disrupts synaptic information transmission, but in extremis leads to extracellular glutamate accumulation and excitotoxicity. A key facet of EAAT1/2 expression in astrocytes is a requirement for signals from other brain cell types in order to maintain their expression. Recent evidence has shown a prominent role for contact-dependent neuron-to-astrocyte and/or endothelial cell-to-astrocyte Notch signalling for inducing and maintaining the expression of these astrocytic glutamate transporters. The relevance of this non-cell-autonomous dependence to age- and neurodegenerative disease-associated decline in astrocytic EAAT expression is discussed, plus the implications for disease progression and putative therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Astrocyte; EAAT1; EAAT2; excitotoxicity; glutamate; neurodegenerative disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil up-regulates astrocytic glutamate transport subsequent to actin remodelling in murine cultured astrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;163(3):533-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01259.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21309758 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte membrane properties are altered in a rat model of developmental cortical malformation but single-cell astrocytic glutamate uptake is robust.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 May;89:157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.02.012. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 26875663 Free PMC article.
-
The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 15;161:107559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30851309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression of the glutamate re-uptake transporter excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (EAAT1) in the normal human CNS and in motor neurone disease: an immunohistochemical study.Neuroscience. 2002;109(1):27-44. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00437-7. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 11784698
-
HIV-1, methamphetamine and astrocyte glutamate regulation: combined excitotoxic implications for neuro-AIDS.Curr HIV Res. 2012 Jul;10(5):392-406. doi: 10.2174/157016212802138832. Curr HIV Res. 2012. PMID: 22591363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of Bmal1 impairs the glutamatergic light input to the SCN in mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Feb 27;19:1538985. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1538985. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40083633 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting patterns of extrasynaptic NMDAR-GluN2B expression in macaque subgenual cingulate and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices.Front Neuroanat. 2025 Apr 4;19:1553056. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2025.1553056. eCollection 2025. Front Neuroanat. 2025. PMID: 40255911 Free PMC article.
-
The development of a high-throughput acoustic droplet ejection mass-spectrometry assay and a solid-supported membrane (SSM)-based electrophysiological assay to study the pharmacological inhibition of SLC1-A3, -A2 and -A1 in a drug discovery program.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1544682. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1544682. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308755 Free PMC article.
-
Major-depressive-disorder-associated dysregulation of ZBTB7A in orbitofrontal cortex promotes astrocyte-mediated stress susceptibility.Neuron. 2025 Jun 11:S0896-6273(25)00394-0. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.05.023. Online ahead of print. Neuron. 2025. PMID: 40516534 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal MML-1/MXL-2 regulates systemic aging via glutamate transporter and cell nonautonomous autophagic and peroxidase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 26;120(39):e2221553120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221553120. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37722055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wahl A.-S., Buchthal B., Rode F., Bomholt S., Freitag H., Hardingham G.E., Rønn L., Bading H. Hypoxic/ischemic conditions induce expression of the putative pro-death gene Clca1 via activation of extrasynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Neuroscience. 2009;158:344–352. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

