Addition of Lymphatic Stimulating Self-Care Practices Reduces Acute Attacks among People Affected by Moderate and Severe Lower-Limb Lymphedema in Ethiopia, a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33348721
- PMCID: PMC7766500
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9124077
Addition of Lymphatic Stimulating Self-Care Practices Reduces Acute Attacks among People Affected by Moderate and Severe Lower-Limb Lymphedema in Ethiopia, a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
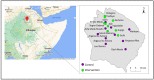
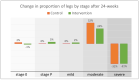
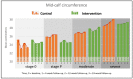
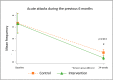
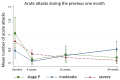
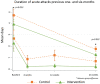
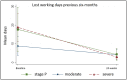
Lymphedema causes disability and exacerbates poverty in many countries. The management of lymphatic filariasis (LF) and podoconiosis-related lymphedema involves daily hygiene to reduce secondary infections, but self-massage and deep-breathing, which have proven beneficial in cancer-related lymphedema, are not included. A cluster randomized trial in northern Ethiopia investigated the effects of lymphatic stimulation for people affected by moderate to severe lymphedema. Participants were allocated to either standard (control n = 59) or enhanced (intervention n = 67) self-care groups. Primary outcomes were lymphedema stage, mid-calf circumference, and tissue compressibility. Secondary outcomes were the frequency and duration of acute attacks. After 24 weeks, fewer patients were assessed as severe (control -37.8%, intervention -42.4%, p = 0.15) and there were clinically relevant changes in mid-calf tissue compressibility but not circumference. There was a significant between-group difference in patients who reported any acute attacks over the study period (control n = 22 (38%), intervention n = 7 (12%), p = 0.014). Daily lymphedema self-care resulted in meaningful benefits for all participants with a greater reduction in acute episodes among people performing lymphatic stimulation. Observations of a change in lymphedema status support earlier findings in Bangladesh and extend the demonstrated benefits of enhanced self-care to people affected by podoconiosis.
Keywords: breathing; exercise; filariasis; lower limb; lymphatic massage; lymphedema; podoconiosis; self-care; skin mobilisation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The study sponsor and funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and no input into publication of study outcomes.
Figures



References
-
- WHO . In: Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis. Rio D.F., editor. Department of Communicable Disease Prevention, Control and Eradication; Geneva, Switzerland: 1999. Annual report of lymphatic filariasis 2000.
-
- WHO . Lymphatic Filariasis: Managing Morbidity and Preventing Disability: An Aide-Memoire for National Programme Managers. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

