Extracellular RNAs in Bacterial Infections: From Emerging Key Players on Host-Pathogen Interactions to Exploitable Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 33348812
- PMCID: PMC7766527
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249634
Extracellular RNAs in Bacterial Infections: From Emerging Key Players on Host-Pathogen Interactions to Exploitable Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
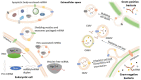
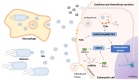
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are key regulators of post-transcriptional gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. These molecules can interact with mRNAs or proteins, affecting a variety of cellular functions. Emerging evidence shows that intra/inter-species and trans-kingdom regulation can also be achieved with exogenous RNAs, which are exported to the extracellular medium, mainly through vesicles. In bacteria, membrane vesicles (MVs) seem to be the more common way of extracellular communication. In several bacterial pathogens, MVs have been described as a delivery system of ncRNAs that upon entry into the host cell, regulate their immune response. The aim of the present work is to review this recently described mode of host-pathogen communication and to foster further research on this topic envisaging their exploitation in the design of novel therapeutic and diagnostic strategies to fight bacterial infections.
Keywords: extracellular RNAs; host-pathogen interactions; membrane vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Host-Pathogen Interactions: A Review of Inter-Kingdom Signaling by Small Noncoding RNA.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 30;12(7):1010. doi: 10.3390/genes12071010. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial RNA in extracellular vesicles: A new regulator of host-pathogen interactions?Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Jul;1863(7):194519. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194519. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32142907 Review.
-
Mammalian microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in the host-bacterial pathogen crosstalk.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 May;65:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27381344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functional RNA cargo of bacterial membrane vesicles.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Mar 1;365(5). doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny023. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29390056 Review.
-
Non-coding RNA regulation in pathogenic bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Nov 12;4:162. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00162. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25429360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Mechanisms Linking Food-Derived MicroRNAs, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Functions in the Context of Nutrition and Human Health.Front Nutr. 2021 Mar 9;8:586564. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.586564. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33768107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the grammar of small RNA secretion using interpretable machine learning.Cell Genom. 2024 Apr 10;4(4):100522. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100522. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 38460515 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptations of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Response to Antibiotic Pressure.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 23;26(11):5025. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115025. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Nosocomial Infections: Multidrug Resistance as a Trigger for the Development of Novel Antimicrobials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;10(8):942. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080942. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34438992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red light-emitting short Mango-based system enables tracking a mycobacterial small noncoding RNA in infected macrophages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 11;51(6):2586-2601. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad100. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36840712 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

