Integrase-Defective Lentiviral Vectors for Delivery of Monoclonal Antibodies against Influenza
- PMID: 33348840
- PMCID: PMC7767071
- DOI: 10.3390/v12121460
Integrase-Defective Lentiviral Vectors for Delivery of Monoclonal Antibodies against Influenza
Abstract
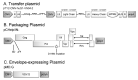
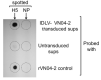
Delivering rapid protection against infectious agents to non-immune populations is a formidable public health challenge. Although passive immunotherapy is a fast and effective method of protection, large-scale production and administration of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is expensive and unpractical. Viral vector-mediated delivery of mAbs offers an attractive alternative to their direct injection. Integrase-defective lentiviral vectors (IDLV) are advantageous for this purpose due to the absence of pre-existing anti-vector immunity and the safety features of non-integration and non-replication. We engineered IDLV to produce the humanized mAb VN04-2 (IDLV-VN04-2), which is broadly neutralizing against H5 influenza A virus (IAV), and tested the vectors' ability to produce antibodies and protect from IAV in vivo. We found that IDLV-transduced cells produced functional VN04-2 mAbs in a time- and dose-dependent fashion. These mAbs specifically bind the hemagglutinin (HA), but not the nucleoprotein (NP) of IAV. VN04-2 mAbs were detected in the serum of mice at different times after intranasal (i.n.) or intramuscular (i.m.) administration of IDLV-VN04-2. Administration of IDLV-VN04-2 by the i.n. route provided rapid protection against lethal IAV challenge, although the protection did not persist at later time points. Our data suggest that administration of mAb-expressing IDLV may represent an effective strategy for rapid protection against infectious diseases.
Keywords: genetic immunization; influenza; integrase-defective lentiviral vector; monoclonal antibody; passive immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
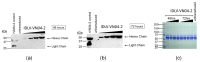
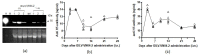
References
-
- BenAmmar-Ceccoli S., Humblot S., Crouzier R., Acres B., Kieny M.P., Herlyn D., Pasquali J.L., Martin T. Recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing immunoglobulin variable regions efficiently and selectively protect mice against tumoral B-cell growth. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001;8:815–826. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700376. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

