β-Catenin Regulates Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Sedentary and Trained Mice
- PMID: 33348907
- PMCID: PMC7766208
- DOI: 10.3390/life10120357
β-Catenin Regulates Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Sedentary and Trained Mice
Abstract
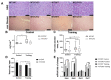
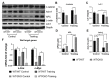
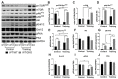
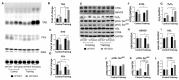
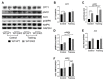
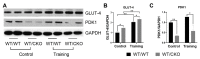
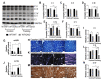
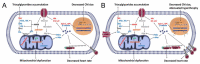
The role of canonical Wnt signaling in metabolic regulation and development of physiological cardiac hypertrophy remains largely unknown. To explore the function of β-catenin in the regulation of cardiac metabolism and physiological cardiac hypertrophy development, we used mice heterozygous for cardiac-specific β-catenin knockout that were subjected to a swimming training model. β-Catenin haploinsufficient mice subjected to endurance training displayed a decreased β-catenin transcriptional activity, attenuated cardiomyocytes hypertrophic growth, and enhanced activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), phosphoinositide-3-kinase-Akt (Pi3K-Akt), and mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (MAPK/Erk1/2) signaling pathways compared to trained wild type mice. We further observed an increased level of proteins involved in glucose aerobic metabolism and β-oxidation along with perturbed activity of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation complexes (OXPHOS) in trained β-catenin haploinsufficient mice. Taken together, Wnt/β-catenin signaling appears to govern metabolic regulatory programs, sustaining metabolic plasticity in adult hearts during the adaptation to endurance training.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signaling; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; oxidative phosphorylation; training-induced heart hypertrophy; β-oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions, or policies of the institutions with which they are affiliated. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Iemitsu M., Miyauchi T., Maeda S., Sakai S., Fujii N., Miyazaki H., Kakinuma Y., Matsuda M., Yamaguchi I. Cardiac Hypertrophy by Hypertension and Exercise Training Exhibits Different Gene Expression of Enzymes in Energy Metabolism. Hypertens. Res. 2003;26:829–837. doi: 10.1291/hypres.26.829. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dobrzyn P., Pyrkowska A., Duda M.K., Bednarski T., Maczewski M., Langfort J., Dobrzyn A. Expression of lipogenic genes is upregulated in the heart with exercise training-induced but not pressure overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013;304:E1348–E1358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00603.2012. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- № 50/4.3 from 01.08.2014/Grant of President of Ukraine for Gifted Youth
- N40/2015-2020/National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine
- UMO-2014/13/B/NZ4/00199, UMO-2016/22/E/NZ4/00650, UMO-2017/27/N/NZ4/01995 and UMO-2015/17/D/NZ5/03446/National Science Centre, Poland
- 665735 (Bio4Med)/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under Marie Sklodowska-Curie
- 3548/H2020/COFUND/2016/2/Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

