Big-Data Glycomics: Tools to Connect Glycan Biosynthesis to Extracellular Communication
- PMID: 33349503
- PMCID: PMC7954846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.10.004
Big-Data Glycomics: Tools to Connect Glycan Biosynthesis to Extracellular Communication
Abstract
Characteristically, cells must sense and respond to environmental cues. Despite the importance of cell-cell communication, our understanding remains limited and often lacks glycans. Glycans decorate proteins and cell membranes at the cell-environment interface, and modulate intercellular communication, from development to pathogenesis. Providing further challenges, glycan biosynthesis and cellular behavior are co-regulating systems. Here, we discuss how glycosylation contributes to extracellular responses and signaling. We further organize approaches for disentangling the roles of glycans in multicellular interactions using newly available datasets and tools, including glycan biosynthesis models, omics datasets, and systems-level analyses. Thus, emerging tools in big data analytics and systems biology are facilitating novel insights on glycans and their relationship with multicellular behavior.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cell–cell interaction; extracellular matrix; glycobiology; glycomics; systems biology.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


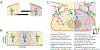
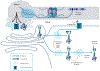
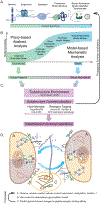
References
-
- Davies HW, Trotter MD. Synthesis and turnover of membrane glycoconjugates in monolayer culture of pig and human epidermal cells. Br J Dermatol. 1981; 104: 649–658. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Palomo A, Braislovsky C, Bernhard W. Ultrastructural modifications of the cell surface and intercellular contacts of some transformed cell strains. Cancer Res. 1969;29: 925–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

