Visualizing the metazoan proliferation-quiescence decision in vivo
- PMID: 33350383
- PMCID: PMC7880687
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.63265
Visualizing the metazoan proliferation-quiescence decision in vivo
Abstract
Cell proliferation and quiescence are intimately coordinated during metazoan development. Here, we adapt a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) sensor to uncouple these key events of the cell cycle in Caenorhabditis elegans and zebrafish through live-cell imaging. The CDK sensor consists of a fluorescently tagged CDK substrate that steadily translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to increasing CDK activity and consequent sensor phosphorylation. We show that the CDK sensor can distinguish cycling cells in G1 from quiescent cells in G0, revealing a possible commitment point and a cryptic stochasticity in an otherwise invariant C. elegans cell lineage. Finally, we derive a predictive model of future proliferation behavior in C. elegans based on a snapshot of CDK activity in newly born cells. Thus, we introduce a live-cell imaging tool to facilitate in vivo studies of cell-cycle control in a wide-range of developmental contexts.
Keywords: C. elegans; CDK sensor; G1/G0; cell biology; cell cycle; cell proliferation; developmental biology; quiescence; zebrafish.
Plain language summary
All living things are made up of cells that form the different tissues, organs and structures of an organism. The human body, for example, is thought to consist of some 37 trillion cells and harbor over 200 cell types. To maintain a working organism, cells divide to create new cells and replace the ones that have died. Cell division is a tightly controlled process consisting of several steps, and cells continuously face a Shakespearean dilemma of deciding whether to continue dividing (also known as cell proliferation) or to halt the process (known as quiescence). This difficult balancing act is critical during all stages of life, from embryonic development to tissue growth in an adult. Problems in the underlying pathways can result in diseases such as cancer. Cell division is driven by proteins called CDKs, which help cells to complete their cell cycle in the correct sequence. To gain more insight into this complex process, scientists have developed tools for monitoring CDKs. One such tool is a fluorescent biosensor, a molecule that can be inserted into cells that glows and moves in response to CDK activity. The biosensor can be studied and measured in each cell using a microscope. Adikes, Kohrman, Martinez et al. adapted and optimized an existing CDK biosensor to help study cell division and the switch between proliferation and quiescence in two common research organisms, the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and the zebrafish. Analysis of this biosensor showed that CDK activity at the end of cell division is higher if the cells will divide again but is low if the cells are going to become quiescent. This could suggest that the decision of a cell between proliferation and quiescence may happen earlier than expected. The optimized biosensor is sensitive enough to detect these differences and can even measure variations that influence proliferation in a region on C. elegans that was once thought to be unchanging. The development of this biosensor provides a useful research tool that could be used in other living organisms. Many research questions relate to cell division and so the applications of this tool are wide ranging.
© 2020, Adikes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RA, AK, MM, NP, JS, TM, MM, MS, OA, NK, SL, RM, NW, QZ, WZ, JF, MB, AP, SS, BM, DM No competing interests declared
Figures

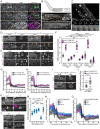
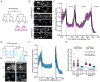
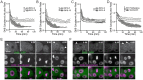
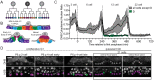
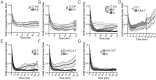
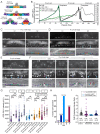
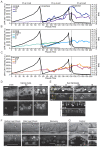
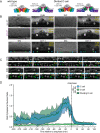
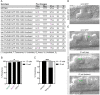
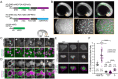
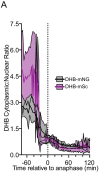

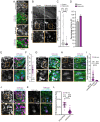

Comment in
-
Deciding when to exit.Elife. 2021 Feb 12;10:e66591. doi: 10.7554/eLife.66591. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33576741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajar BT, Lam AJ, Badiee RK, Oh YH, Chu J, Zhou XX, Kim N, Kim BB, Chung M, Yablonovitch AL, Cruz BF, Kulalert K, Tao JJ, Meyer T, Su XD, Lin MZ. Fluorescent indicators for simultaneous reporting of all four cell cycle phases. Nature Methods. 2016;13:993–996. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SSP-2016-1533/Searle Scholars Program
- DP2 CA238330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01GM121597-02S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01GM121597-03S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- IOS 1452928/National Science Foundation
- 1K99GM13548901/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 GM119136/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01GM124282/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM124282/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM133131/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01GM121597/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HD100091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- EP-C-18-008/EPA/EPA/United States
- F31 GM128319/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DRR-47-17/DRCRF/Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation/United States
- T32 GM008444/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 132969-PF-18-226-01-CSM/American Cancer Society
- RSG-18-008-01/American Cancer Society
- K99 GM135489/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM121597/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

