Evaluating the Onset, Severity, and Recovery of Changes to Smell and Taste Associated With COVID-19 Infection in a Singaporean Population (the COVOSMIA-19 Trial): Protocol for a Prospective Case-Control Study
- PMID: 33351775
- PMCID: PMC7781589
- DOI: 10.2196/24797
Evaluating the Onset, Severity, and Recovery of Changes to Smell and Taste Associated With COVID-19 Infection in a Singaporean Population (the COVOSMIA-19 Trial): Protocol for a Prospective Case-Control Study
Abstract
Background: Sudden loss of smell and/or taste has been suggested to be an early marker of COVID-19 infection, with most findings based on self-reporting of sensory changes at a single time point.
Objective: To understand the onset, severity, and recovery of sensory changes associated with COVID-19 infection, this study will longitudinally track changes in chemosensory acuity among people with suspected COVID-19 infection using standardized test stimuli that are self-administered over 28 days.
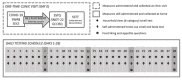
Methods: In a prospective, case-controlled observational study, volunteers will be recruited when they present for COVID-19 screening by respiratory tract polymerase chain reaction test ("swab test"). The volunteers will initially complete a series of questionnaires to record their recent changes in smell and taste ability, followed by a brief standardized smell and taste test. Participants will receive a home-use smell and taste test kit to prospectively complete daily self-assessments of their smell and taste acuity at their place of residence for up to 4 weeks, with all data submitted for collection through web-based software.
Results: This study has been approved by the Domain Specific Review Board of the National Healthcare Group, Singapore, and is funded by the Biomedical Research Council Singapore COVID-19 Research Fund. Recruitment began on July 23, 2020, and will continue through to March 31, 2021. As of October 2, 2020, 69 participants had been recruited.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this study will be the first to collect longitudinal data on changes to smell and taste sensitivity related to clinically diagnosed COVID-19 infection, confirmed by PCR swab test, in a population-based cohort. The findings will provide temporal insights on the onset, severity, and recovery of sensory changes with COVID-19 infection, the consistency of symptoms, and the frequency of full smell recovery among patients with COVID-19. This self-administered and cost-effective approach has many advantages over self-report questionnaire-based methods and provides a more objective measure of smell and taste changes associated with COVID-19 infection; this will encourage otherwise asymptomatic individuals who are potential spreaders of the virus to self-isolate and seek formal medical diagnosis if they experience a sudden change in sensory acuity. This broadened case finding can potentially help control the COVID-19 pandemic and reduce the emergence of clusters of infections.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04492904; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04492904.
International registered report identifier (irrid): DERR1-10.2196/24797.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; ageusia; anosmia; dysfunction; gustatory dysfunction; infectious disease; marker; monitoring; olfactory dysfunction; onset; protocol; recovery; severity; smell; symptom; taste.
©Florence Sheen, Vicki Tan, Sumanto Haldar, Sharmila Sengupta, David Allen, Jyoti Somani, Hui Yee Chen, Paul Tambyah, Ciaran G Forde. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (http://www.researchprotocols.org), 31.12.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Loss of Sense of Smell as Marker of COVID-19 Infection. ENT UK. 2020. [2020-12-23]. https://www.entuk.org/sites/default/files/files/Loss%20of%20sense%20of%2....
-
- Advice for patients with new-onset anosmia during COVID-19 pandemic. ENT UK. [2020-07-17]. https://www.entuk.org/advice-patients-new-onset-anosmia-during-covid-19-....
-
- Anosmia, Hyposmia, and Dysgeusia Symptoms of Coronavirus Disease. American Academy of Otolaryngology. 2020. [2020-07-16]. https://www.entnet.org/content/aao-hns-anosmia-hyposmia-and-dysgeusia-sy....
-
- Anosmia Alert COVID-19. French Society of ENT. 2020. [2020-07-17]. https://www.sforl.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Alerte-anosmie-COVID-19....
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous