Clinical Biofilm Ring Test® Reveals the Potential Role of β-Lactams in the Induction of Biofilm Formation by P. aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Patients
- PMID: 33352641
- PMCID: PMC7766936
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9121065
Clinical Biofilm Ring Test® Reveals the Potential Role of β-Lactams in the Induction of Biofilm Formation by P. aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Patients
Abstract
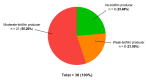
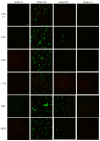
Biofilms are characterized by high tolerance to antimicrobials. However, conventional antibiograms are performed on planktonic microorganisms. Through the clinical Biofilm Ring Test® (cBRT), initially aimed to measure the adhesion propensity of bacteria, we discerned a variable distribution of biofilm-producer strains among P. aeruginosa samples isolated from expectorations of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. Despite a majority of spontaneous adherent isolates, few strains remained planktonic after 5 h of incubation. Their analysis by an adapted protocol of the cBRT revealed an induction of the biofilm early formation by sub-inhibitory doses of β-lactams. Microscopic observations of bacterial cultures stained with Syto 9/Propidium Iodide (PI) confirmed the ability of antimicrobials to increase either the bacterial biomass or the biovolume occupied by induced sessile cells. Finally, the cBRT and its derivatives enabled to highlight in a few hours the potential inducer property of antibiotics on bacterial adhesion. This phenomenon should be considered carefully in the context of CF since patients are constantly under fluctuating antimicrobial treatments. To conclude, assays derived from the Biofilm Ring Test® (BRT) device, not only define efficient doses preventing biofilm formation, but could be useful for the antimicrobial selection in CF, to avoid inducer molecules of the early biofilm initiation.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibiotics; biofilm; clinical Biofilm Ring Test®; cystic fibrosis; early bacterial adhesion induction.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors E.O., C.P., S.B.-B., and J.T. were employed by the companies BioFilm Pharma SAS and BioFilm Control SAS. Author T.B. is the inventor of the BRT device. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nathwani D., Raman G., Sulham K., Gavaghan M., Menon V. Clinical and economic consequences of hospital-acquired resistant and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2014;3:32. doi: 10.1186/2047-2994-3-32. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

