Ketogenic Diet: Impact on Cellular Lipids in Hippocampal Murine Neurons
- PMID: 33352829
- PMCID: PMC7766526
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12123870
Ketogenic Diet: Impact on Cellular Lipids in Hippocampal Murine Neurons
Abstract
Background: The mechanism of action of the ketogenic diet (KD), an effective treatment for pharmacotherapy refractory epilepsy, is not fully elucidated. The present study examined the effects of two metabolites accumulating under KD-beta-hydroxybutyrate (ßHB) and decanoic acid (C10) in hippocampal murine (HT22) neurons.
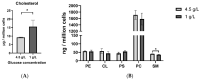
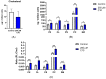
Methods: A mouse HT22 hippocampal neuronal cell line was used in the present study. Cellular lipids were analyzed in cell cultures incubated with high (standard) versus low glucose supplemented with ßHB or C10. Cellular cholesterol was analyzed using HPLC, while phospholipids and sphingomyelin (SM) were analyzed using HPTLC.
Results: HT22 cells showed higher cholesterol, but lower SM levels in the low glucose group without supplements as compared to the high glucose groups. While cellular cholesterol was reduced in both ßHB- and C10-incubated cells, phospholipids were significantly higher in C10-incubated neurons. Ratios of individual phospholipids to cholesterol were significantly higher in ßHB- and C10-incubated neurons as compared to controls.
Conclusion: Changes in the ratios of individual phospholipids to cholesterol in HT22 neurons suggest a possible alteration in the composition of the plasma membrane and organelle membranes, which may provide insight into the working mechanism of KD metabolites ßHB and C10.
Keywords: cholesterol; decanoic acid; hydroxybutyrate; ketogenic diet; neurons; phospholipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Blusztajn J.K., Liscovitch M., Mauron C., Richardson U.I., Wurtman R.J. Phosphatidylcholine as a precursor of choline for acetylcholine synthesis. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1987;24:247–259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

