Pyrrolidinium Containing Ionic Liquid Electrolytes for Li-Based Batteries
- PMID: 33352999
- PMCID: PMC7766901
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25246002
Pyrrolidinium Containing Ionic Liquid Electrolytes for Li-Based Batteries
Abstract
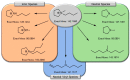
Ionic liquids are potential alternative electrolytes to the more conventional solid-state options under investigation for future energy storage solutions. This review addresses the utilization of IL electrolytes in energy storage devices, particularly pyrrolidinium-based ILs. These ILs offer favorable properties, such as high ionic conductivity and the potential for high power drain, low volatility and wide electrochemical stability windows (ESW). The cation/anion combination utilized significantly influences their physical and electrochemical properties, therefore a thorough discussion of different combinations is outlined. Compatibility with a wide array of cathode and anode materials such as LFP, V2O5, Ge and Sn is exhibited, whereby thin-films and nanostructured materials are investigated for micro energy applications. Polymer gel electrolytes suitable for layer-by-layer fabrication are discussed for the various pyrrolidinium cations, and their compatibility with electrode materials assessed. Recent advancements regarding the modification of typical cations such a 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium, to produce ether-functionalized or symmetrical cations is discussed.
Keywords: anode; cathode; electrolyte; energy storage; ionic liquids; lithium ion batteries; lithium metal batteries; polymer gel electrolyte; pyrrolidinium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


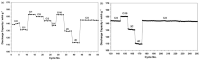
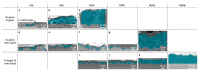
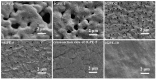
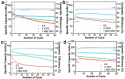

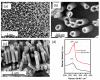
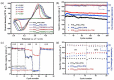
References
-
- Statista Internet of Things (IoT) Connected Devices Installed Base Worldwide from 2015 to 2025 (In Billions) [(accessed on 27 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/471264/iot-number-of-connected-devic...
-
- Cook-Chennault K.A., Thambi N., Sastry A.M. Powering MEMS portable devices—A review of non-regenerative and regenerative power supply systems with special emphasis on piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008;17:043001. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/17/4/043001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

