Epidemic Dynamics via Wavelet Theory and Machine Learning with Applications to Covid-19
- PMID: 33353045
- PMCID: PMC7767158
- DOI: 10.3390/biology9120477
Epidemic Dynamics via Wavelet Theory and Machine Learning with Applications to Covid-19
Abstract
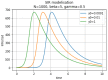
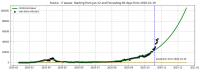
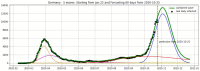
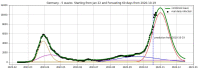
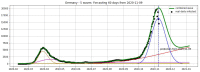
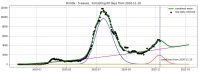
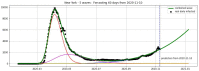
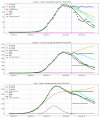
We introduce the concept of epidemic-fitted wavelets which comprise, in particular, as special cases the number I(t) of infectious individuals at time t in classical SIR models and their derivatives. We present a novel method for modelling epidemic dynamics by a model selection method using wavelet theory and, for its applications, machine learning-based curve fitting techniques. Our universal models are functions that are finite linear combinations of epidemic-fitted wavelets. We apply our method by modelling and forecasting, based on the Johns Hopkins University dataset, the spread of the current Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic in France, Germany, Italy and the Czech Republic, as well as in the US federal states New York and Florida.
Keywords: Covid-19; Covid-19 spread predicting; SARS-CoV-2; curve fitting; epidemic dynamics; epidemic-fitted wavelet; model selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Brauer F., van den Driessche P., Wu J., editors. Lecture Notes in Mathematics 1945, Mathematical Biosciences Subseries. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2008. Mathematical epidemiology.
-
- Kermack W.O., McKendrick A.G. A Contribution to the Mathematical Theory of Epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. 1927;115:700–721.
-
- Bartlett M.S. Deterministic and stochastic models for recurrent epidemics; Proceedings of the Third Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability; Berkeley, CA, USA. 23–25 December 1956; pp. 81–109.
-
- Bartlett M.S. Measles periodicity and community size. J. R. Stat. Soc. A. 1957;120:48–70. doi: 10.2307/2342553. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

