Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Premolar Teeth in a Kuwaiti Subpopulation: A CBCT Clinical Study
- PMID: 33353914
- PMCID: PMC7881383
- DOI: 10.14744/eej.2020.40085
Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Premolar Teeth in a Kuwaiti Subpopulation: A CBCT Clinical Study
Abstract
Objective: To study the root and root canal morphology of mandibular premolars in a Kuwaiti subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods: 152 CBCT images were obtained from the radiology department archives of four dental centers in Kuwait. A total of 476 mandibular premolar teeth were analyzed by two observers. The number of roots, root canal configuration types and canal curvature measurements were examined. The relationship between sex, tooth position, and incidence of an additional canal were compared using the chi-square test, and the level of significance was set at 0.05 (P=0.05).
Results: The number of roots in mandibular first premolars was one in 73.9%, two in 24.9%, three and four in 1.2%. On the other hand, the number of roots in mandibular second premolars was one in 79.2% and two in 20.8%. Based on Vertucci's classification system, 18.7% of the teeth were type II followed by type VI (14.3%). The majority of the examined teeth were straight (74.8%) and the incidence of distal root angulation was about 21%. Canal configurations not included in the Vertucci classification were reported in 102 teeth (21.4%). Variability was significantly higher in the second premolars compared to first premolar (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The Kuwaiti population has complex root canal morphology in mandibular premolar teeth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

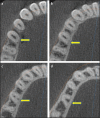
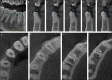

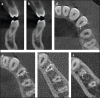

References
-
- Vertucci FJ. Root canal morphology of mandibular premolars. J Am Dent Assoc. 1978;97(1):47–50. - PubMed
-
- Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;58(5):589–99. - PubMed
-
- Cantatore G, Berutti E, Castellucci A. Missed anatomy:Frequency and clinical impact. Endod Topics. 2006;15(1):3–31.
-
- Slowey RR. Root canal anatomy. Road map to successful endodontics. Dent Clin North Am. 1979;23(4):555–573. - PubMed
-
- Lee YY, Yeh PY, Pai SF, Yang SF. Maxillary first molar with six canals. J Dent Sci. 2009;4(4):198–201.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

