Anesthetic Efficacy of Lidocaine/Ketorolac in Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block in Patients with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33353921
- PMCID: PMC7881381
- DOI: 10.14744/eej.2020.74946
Anesthetic Efficacy of Lidocaine/Ketorolac in Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block in Patients with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this randomized, double-blind study was to evaluate the anesthetic efficacy of lidocaine-ketorolac administration by Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block (IANB) in patients with irreversible pulpitis.
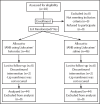
Methods: Eighty-eight adult patients received a combination of either one cartridge of '2% lidocaine with 1: 80.000 epinephrine' (Li) plus one cartridge of a mixture of 0.8 mL of the same solution and 1mL ketorolac tromethamine (KT)(30 mg/mL), or one cartridge of Li solution plus one cartridge of a mixture of the same solution and saline. Endodontic access was prepared after fifteen minutes. Anesthetic success was defined as no or mild pain [less than 54 mm on the Heft-Parker visual analog scale (HP-VAS)] during access cavity preparation and initial file insertion. Chi-square test was used for data analysis, and the level of significance was set at 0.05 (P=0.05).
Results: Results showed that the success rates were 34.1% and 27.3% for Li-KT and Li-Saline groups, respectively, with no significant difference between the two groups (P=0.48). However, significant decrease of baseline mean VAS pain score of the participants in both groups was found during access cavity preparation or initial file insertion (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Mixed Li-KT solution did not increase the success rate of IANB injection significantly.
Conflict of interest statement
Similar articles
-
Comparative Evaluation of Anesthetic Efficacy of 2% Lidocaine, 4% Articaine, and 0.5% Bupivacaine on Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block in Patients with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial.J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2017 Spring;31(2):124-128. doi: 10.11607/ofph.1642. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2017. PMID: 28437508 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of oral premedication of meloxicam, ketorolac, dexamethasone, and ibuprofen on the success rate of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Quintessence Int. 2023 Feb 10;54(2):92-99. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.b3605097. Quintessence Int. 2023. PMID: 36421046 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative evaluation of effect of preoperative oral medication of ibuprofen and ketorolac on anesthetic efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block with lidocaine in patients with irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial.J Endod. 2010 Mar;36(3):375-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.11.010. J Endod. 2010. PMID: 20171350 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Preoperative Oral Ketorolac on Anesthetic Efficacy of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block and Buccal and Lingual Infiltration with Articaine and Lidocaine in Patients with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, Double-blind Study.J Endod. 2015 Nov;41(11):1773-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Sep 26. J Endod. 2015. PMID: 26410153 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of sodium bicarbonate-buffered lidocaine on the success of inferior alveolar nerve block for teeth with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, randomized double-blind study.J Endod. 2015 Jan;41(1):33-5. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Oct 31. J Endod. 2015. PMID: 25442722 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Preoperative Analgesics on the Efficacy of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block with Patients Having Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial.Eur Endod J. 2023 Aug;8(4):246-252. doi: 10.14744/eej.2023.42650. Eur Endod J. 2023. PMID: 38219036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Addition of 2 mg dexamethasone to improve the anesthetic efficacy of 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine administered for inferior alveolar nerve block to patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in the mandibular molars: a randomized double-blind clinical trial.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2022 Aug;22(4):305-314. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2022.22.4.305. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 35991360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal V, Singla M, Rizvi A, Miglani S. Comparative evaluation of local infiltration of articaine articaine plus ketorolac and dexamethasone on anesthetic efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block with lidocaine in patients with irreversible pulpitis. J Endod. 2011;37(4):445–9. - PubMed
-
- Akhlaghi NM, Hormozi B, Abbott PV, Khalilak Z. Efficacy of Ketorolac Buccal Infiltrations and Inferior Alveolar Nerve Blocks in Patients with Irreversible Pulpitis:A Prospective Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J Endod. 2016;42(5):691–5. - PubMed
-
- Oleson M, Drum M, Reader A, Nusstein J, Beck M. Effect of preoperative ibuprofen on the success of the inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis. J Endod. 2010;36(3):379–82. - PubMed
-
- Prasanna N, Subbarao CV, Gutmann JL. The efficacy of pre-operative oral medication of lornoxicam and diclofenac potassium on the success of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis:a double-blind randomised controlled clinical trial. Int Endod J. 2011;44(4):330–6. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal V, Singla M, Kabi D. Comparative evaluation of effect of preoperative oral medication of ibuprofen and ketorolac on anesthetic efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block with lidocaine in patients with irreversible pulpitis:a prospective double-blind, randomized clinical trial. J Endod. 2010;36(3):375–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous