Cellular birthdate predicts laminar and regional cholinergic projection topography in the forebrain
- PMID: 33355093
- PMCID: PMC7758062
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.63249
Cellular birthdate predicts laminar and regional cholinergic projection topography in the forebrain
Abstract
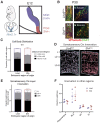
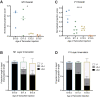
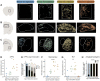
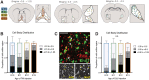
The basal forebrain cholinergic system projects broadly throughout the cortex and constitutes a critical source of neuromodulation for arousal and attention. Traditionally, this system was thought to function diffusely. However, recent studies have revealed a high degree of spatiotemporal specificity in cholinergic signaling. How the organization of cholinergic afferents confers this level of precision remains unknown. Here, using intersectional genetic fate mapping, we demonstrate that cholinergic fibers within the mouse cortex exhibit remarkable laminar and regional specificity and that this is organized in accordance with cellular birthdate. Strikingly, birthdated cholinergic projections within the cortex follow an inside-out pattern of innervation. While early born cholinergic populations target deep layers, late born ones innervate superficial laminae. We also find that birthdate predicts cholinergic innervation patterns within the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. Our work reveals previously unappreciated specificity within the cholinergic system and the developmental logic by which these circuits are assembled.
Keywords: basal forebrain; cholinergic; cortex; developmental biology; mouse; neuroscience.
© 2020, Allaway et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KA, WM, RT, MS, JH, BR, RM, GF No competing interests declared
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

