New Family of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules Defined by a Galactosyl-Binding Protein Module from a Cellvibrio japonicus Endo-Xyloglucanase
- PMID: 33355108
- PMCID: PMC8090896
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02634-20
New Family of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules Defined by a Galactosyl-Binding Protein Module from a Cellvibrio japonicus Endo-Xyloglucanase
Abstract
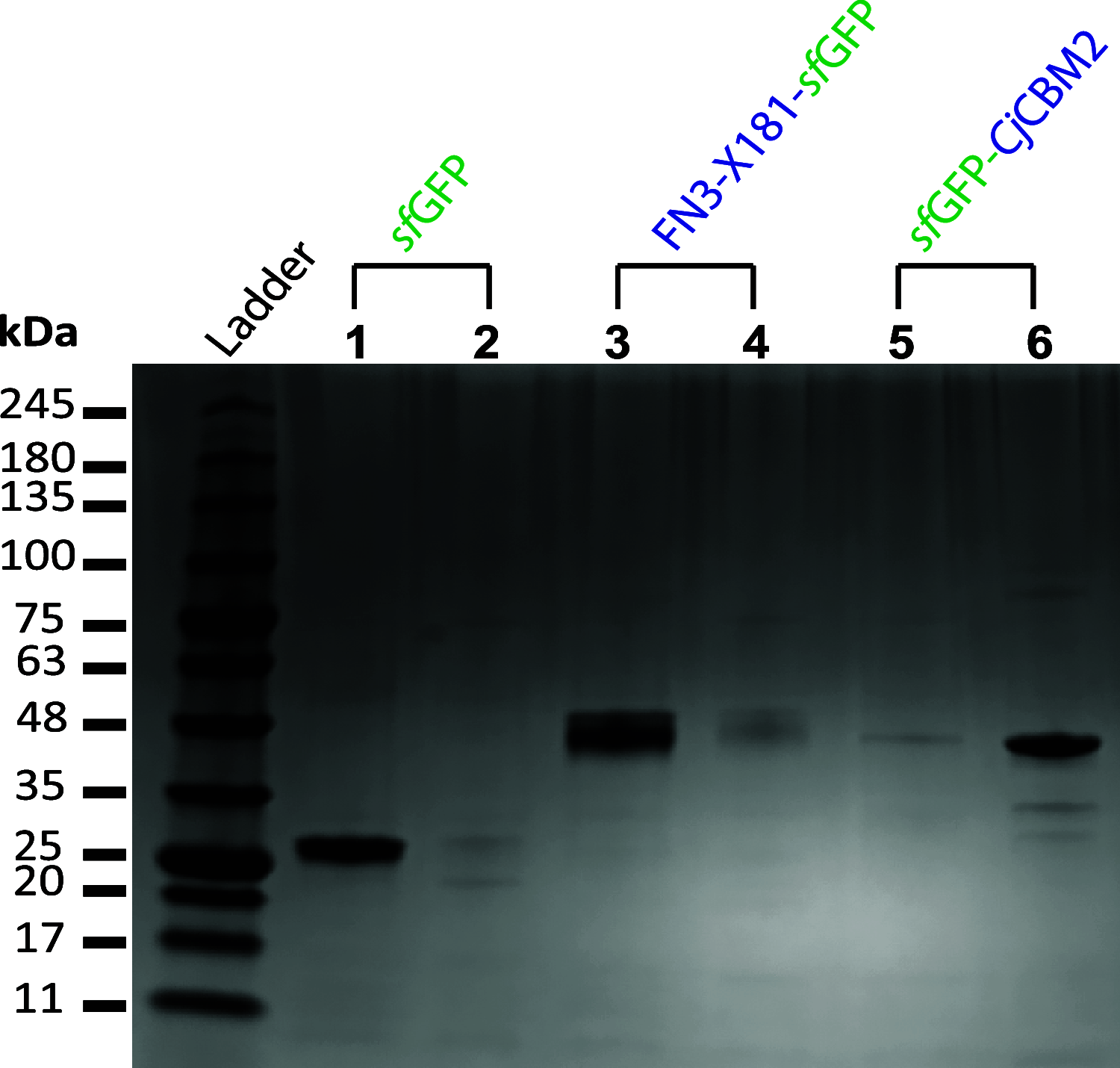
Carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs) are usually appended to carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) and serve to potentiate catalytic activity, for example, by increasing substrate affinity. The Gram-negative soil saprophyte Cellvibrio japonicus is a valuable source for CAZyme and CBM discovery and characterization due to its innate ability to degrade a wide array of plant polysaccharides. Bioinformatic analysis of the CJA_2959 gene product from C. japonicus revealed a modular architecture consisting of a fibronectin type III (Fn3) module, a cryptic module of unknown function (X181), and a glycoside hydrolase family 5 subfamily 4 (GH5_4) catalytic module. We previously demonstrated that the last of these, CjGH5F, is an efficient and specific endo-xyloglucanase (M. A. Attia, C. E. Nelson, W. A. Offen, N. Jain, et al., Biotechnol Biofuels 11:45, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1039-6). In the present study, C-terminal fusion of superfolder green fluorescent protein in tandem with the Fn3-X181 modules enabled recombinant production and purification from Escherichia coli. Native affinity gel electrophoresis revealed binding specificity for the terminal galactose-containing plant polysaccharides galactoxyloglucan and galactomannan. Isothermal titration calorimetry further evidenced a preference for galactoxyloglucan polysaccharide over short oligosaccharides comprising the limit-digest products of CjGH5F. Thus, our results identify the X181 module as the defining member of a new CBM family, CBM88. In addition to directly revealing the function of this CBM in the context of xyloglucan metabolism by C. japonicus, this study will guide future bioinformatic and functional analyses across microbial (meta)genomes. IMPORTANCE This study reveals carbohydrate-binding module family 88 (CBM88) as a new family of galactose-binding protein modules, which are found in series with diverse microbial glycoside hydrolases, polysaccharide lyases, and carbohydrate esterases. The definition of CBM88 in the carbohydrate-active enzymes classification (http://www.cazy.org/CBM88.html) will significantly enable future microbial (meta)genome analysis and functional studies.
Keywords: Bacteroidetes; Cellvibrio; Gammaproteobacteria; carbohydrate-active enzyme; carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs); glycoside hydrolase; mannan; plant biomass; polysaccharide; xyloglucan; xyloglucanase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional and structural characterization of a potent GH74 endo-xyloglucanase from the soil saprophyte Cellvibrio japonicus unravels the first step of xyloglucan degradation.FEBS J. 2016 May;283(9):1701-19. doi: 10.1111/febs.13696. Epub 2016 Mar 30. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26929175
-
The modular architecture of Cellvibrio japonicus mannanases in glycoside hydrolase families 5 and 26 points to differences in their role in mannan degradation.Biochem J. 2003 May 1;371(Pt 3):1027-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021860. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12523937 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo characterization of three Cellvibrio japonicus glycoside hydrolase family 5 members reveals potent xyloglucan backbone-cleaving functions.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Feb 17;11:45. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1039-6. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 29467823 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide degradation systems of the saprophytic bacterium Cellvibrio japonicus.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Jul;32(7):121. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2068-6. Epub 2016 Jun 4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27263016 Review.
-
Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition.Biochem J. 2004 Sep 15;382(Pt 3):769-81. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040892. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15214846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Origins of xyloglucan-degrading enzymes in fungi.New Phytol. 2025 Jan;245(2):458-464. doi: 10.1111/nph.20251. Epub 2024 Nov 17. New Phytol. 2025. PMID: 39550623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of WxL and S-Layer Proteins from Lactobacillus brevis with the Ability to Bind Cellulose and Xylan.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4136. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084136. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456954 Free PMC article.
-
Ephedra sinica polysaccharide regulate the anti-inflammatory immunity of intestinal microecology and bacterial metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 23;15:1414675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1414675. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38846095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ragauskas AJ, Beckham GT, Biddy MJ, Chandra R, Chen F, Davis MF, Davison BH, Dixon RA, Gilna P, Keller M, Langan P, Naskar AK, Saddler JN, Tschaplinski TJ, Tuskan GA, Wyman CE. 2014. Lignin valorization: improving lignin processing in the biorefinery. Science 344:1246843. doi:10.1126/science.1246843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

