Termini restraining of small membrane proteins enables structure determination at near-atomic resolution
- PMID: 33355146
- PMCID: PMC11205269
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe3717
Termini restraining of small membrane proteins enables structure determination at near-atomic resolution
Abstract
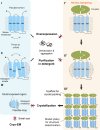
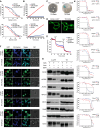
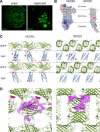
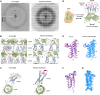
Small membrane proteins are difficult targets for structural characterization. Here, we stabilize their folding by restraining their amino and carboxyl termini with associable protein entities, exemplified by the two halves of a superfolder GFP. The termini-restrained proteins are functional and show improved stability during overexpression and purification. The reassembled GFP provides a versatile scaffold for membrane protein crystallization, enables diffraction to atomic resolution, and facilitates crystal identification, phase determination, and density modification. This strategy gives rise to 14 new structures of five vertebrate proteins from distinct functional families, bringing a substantial expansion to the structural database of small membrane proteins. Moreover, a high-resolution structure of bacterial DsbB reveals that this thiol oxidoreductase is activated through a catalytic triad, similar to cysteine proteases. Overall, termini restraining proves exceptionally effective for stabilization and structure determination of small membrane proteins.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Kang H. J., Lee C., Drew D., Breaking the barriers in membrane protein crystallography. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 45, 636–644 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Tate C. G., A crystal clear solution for determining G-protein-coupled receptor structures. Trends Biochem. Sci. 37, 343–352 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Magnani F., Serrano-Vega M. J., Shibata Y., Abdul-Hussein S., Lebon G., Miller-Gallacher J., Singhal A., Strege A., Thomas J. A., Tate C. G., A mutagenesis and screening strategy to generate optimally thermostabilized membrane proteins for structural studies. Nat. Protoc. 11, 1554–1571 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y., Morais-Cabral J. H., Kaufman A., MacKinnon R., Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel–Fab complex at 2.0 Å resolution. Nature 414, 43–48 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

