Deciphering the Complex Communication Networks That Orchestrate Pancreatic Islet Function
- PMID: 33355306
- PMCID: PMC7881851
- DOI: 10.2337/dbi19-0033
Deciphering the Complex Communication Networks That Orchestrate Pancreatic Islet Function
Abstract
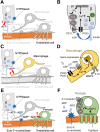
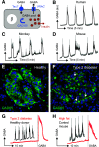
Pancreatic islets are clusters of hormone-secreting endocrine cells that rely on intricate cell-cell communication mechanisms for proper function. The importance of multicellular cooperation in islet cell physiology was first noted nearly 30 years ago in seminal studies showing that hormone secretion from endocrine cell types is diminished when these cells are dispersed. These studies showed that reestablishing cellular contacts in so-called pseudoislets caused endocrine cells to regain hormone secretory function. This not only demonstrated that cooperation between islet cells is highly synergistic but also gave birth to the field of pancreatic islet organoids. Here we review recent advances related to the mechanisms of islet cell cross talk. We first describe new developments that revise current notions about purinergic and GABA signaling in islets. Then we comment on novel multicellular imaging studies that are revealing emergent properties of islet communication networks. We finish by highlighting and discussing recent synthetic approaches that use islet organoids of varied cellular composition to interrogate intraislet signaling mechanisms. This reverse engineering of islets not only will shed light on the mechanisms of intraislet signaling and define communication networks but also may guide efforts aimed at restoring islet function and β-cell mass in diabetes.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

References
-
- Halban PA, Wollheim CB, Blondel B, Meda P, Niesor EN, Mintz DH. The possible importance of contact between pancreatic islet cells for the control of insulin release. Endocrinology 1982;111:86–94 - PubMed
-
- Weir GC, Halban PA, Meda P, Wollheim CB, Orci L, Renold AE. Dispersed adult rat pancreatic islet cells in culture: A, B, and D cell function. Metabolism 1984;33:447–453 - PubMed
-
- Hauge-Evans AC, Squires PE, Persaud SJ, Jones PM. Pancreatic beta-cell-to-beta-cell interactions are required for integrated responses to nutrient stimuli: enhanced Ca2+ and insulin secretory responses of MIN6 pseudoislets. Diabetes 1999;48:1402–1408 - PubMed
-
- Lammert E, Thorn P. The role of the islet niche on beta cell structure and function. J Mol Biol 2020;432:1407–1418 - PubMed

