Liraglutide protects palmitate-induced INS-1 cell injury by enhancing autophagy mediated via FoxO1
- PMID: 33355375
- PMCID: PMC7789139
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11786
Liraglutide protects palmitate-induced INS-1 cell injury by enhancing autophagy mediated via FoxO1
Abstract
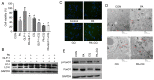
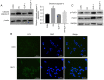
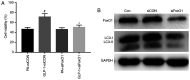
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by insulin resistance and a progressive loss in mass and function of pancreatic β-cells. In T2DM, lipotoxicity leads to β-cells dysfunction and decreases its number. Autophagy serves a crucial role in maintaining the normal islet architecture and the function of β-cells. Moreover, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and its analogs have beneficial roles in pancreatic β-cells. However, the protective effects of GLP-1 agents on palmitate (PA)-induced pancreatic β-cells and their underlying mechanisms are not fully elucidated. Forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) can prevent pancreatic β-cells from apoptosis. Whether GLP-1 protects against PA-induced β-cells injury via FoxO1 remains unknown. The present study exposed INS-1 cells to PA to establish a T2DM injury model. Cell viability was evaluated using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, and apoptosis was determined via western blotting. Furthermore, autophagy was examined using western blotting, immunofluorescence and transmission electron microscopy. Silencing FoxO1 was used to inhibit the activities of FoxO1. The results suggested that the GLP-1 analog liraglutide enhanced the cell viability, inhibited the protein expression of cleaved caspase-3 and increased the expression levels of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain3 (LC3) II/I, and FoxO1 in INS-1 cells. The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine inhibited the protective effects of liraglutide on INS-1 cells. Silencing of FoxO1 decreased the expression levels of LC3-II and attenuated the protection of liraglutide on the viability of INS-1 cells. In conclusion, the results indicated that liraglutide ameliorated the PA-induced islet β-cells injury via the upregulation of autophagy-mediated by FoxO1.
Keywords: T2DM; pancreatic β cells; autophagy; liraglutide; FoxO1.
Figures


References
-
- Chen ZF, Li YB, Han JY, Yin JJ, Wang Y, Zhu LB, Xie GY. Liraglutide prevents high glucose level induced insulinoma cells apoptosis by targeting autophagy. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013;126:937–941. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

