Hyaluronan-Conjugated Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Use
- PMID: 33355448
- PMCID: PMC8243741
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c20088
Hyaluronan-Conjugated Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Use
Abstract
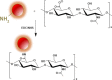
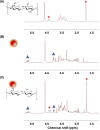
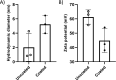
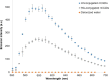
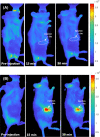
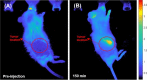
This work demonstrates the application of hyaluronan-conjugated nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (HA-nCQDs) for bioimaging of tumor cells and illustrates their potential use as carriers in targeted drug delivery. Quantum dots are challenging to deliver with specificity, which hinders their application. To facilitate targeted internalization by cancer cells, hyaluronic acid, a natural ligand of CD44 receptors, was covalently grafted on nCQDs. The HA-nCQD conjugate was synthesized by carbodiimide coupling of the amine moieties on nCQDs and the carboxylic acids on HA chains. Conjugated HA-nCQD retained sufficient fluorescence, although with 30% lower quantum efficiency than the original nCQDs. Confocal microscopy showed enhanced internalization of HA-nCQDs, facilitated by CD44 receptors. To demonstrate the specificity of HA-nCQDs toward human tumor cells, patient-derived breast cancer tissue with high-CD44 expression was implanted in adult mice. The tumors were allowed to grow up to 200-250 mm3 prior to the injection of HA-nCQDs. With either local or systemic injection, we achieved a high level of tumor specificity judged by a strong signal-to-noise ratio between the tumor and the surrounding tissue in vivo. Overall, the results show that HA-nCQDs can be used for imaging of CD44-specific tumors in preclinical models of human cancer and potentially used as carriers for targeted drug delivery into CD44-rich cells.
Keywords: CD44 receptors; bioimaging; breast cancer; cancer; carbon quantum dots; hyaluronic acid; tumor imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hola K.; Zhang Y.; Wang Y.; Giannelis E. P.; Zboril R.; Rogach A. L. Carbon dots-Emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.09.004. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

