Opening the black box of non-pharmacological care in systemic sclerosis: a cross-sectional online survey of Dutch health professionals
- PMID: 33355711
- PMCID: PMC8164617
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-020-04765-4
Opening the black box of non-pharmacological care in systemic sclerosis: a cross-sectional online survey of Dutch health professionals
Abstract
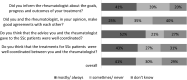
The objective is to describe the spectrum of the health professional (HP) treatment approach for systemic sclerosis (SSc) from the perspective of Dutch HPs, including alignment of treatment goals set by HPs with self-reported referral reasons, coverage of patient-reported unmet care needs, and quality of communication between HPs and rheumatologists. Dutch HPs were invited through their patients with SSc to complete an anonymous online survey. The survey covered referral reasons, treatment goals, and interventions of the last patient treated, as well as the perceived quality of communication between HPs and rheumatologists. Referral reasons and treatment targets were linked to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health following the refined ICF Linking Rules. Seventy-nine HPs from 8 professions (including 58 physiotherapists, 73%) completed the survey. One hundred and thirty-three different referral reasons were reported, yielding 58 different ICF codes, with 41 (70.7%) being linked to the ICF domain "body structures and functions." The reported interventions focused on body functions/structures (27.9%), training of daily activities (25.6%), education and advice (26.3%), and psychosocial interventions (20.2%). The quality of communication between HPs and rheumatologists was perceived as low. Our findings revealed numerous treatment options offered by Dutch HPs addressing the unmet care needs of patients with SSc. There is an overlap in the content of the various HP disciplines, and HP treatment goals are not sufficiently aligned with referrals of rheumatologists. HP treatment offer seemed inefficiently organized, possibly precluding rheumatologists from making targeted referrals. Communication between rheumatologists and HPs should be improved.
Keywords: Cross sectional survey; Health professionals; Systemic sclerosis; Unmet care needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no benefits from commercial sources, no other financial interests, and no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Papelard A, Daste C, Alami S, Sanchez K, Roren A, Segretin F, et al. (2019) Construction of an ICF core set and ICF-based questionnaire assessing activities and participation in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology - PubMed
-
- Peytrignet S, Denton CP, Lunt M, Hesselstrand R, Mouthon L, Silman A, et al. Disability, fatigue, pain and their associates in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: the European Scleroderma Observational Study. Rheumatology. 2017;57:370–381. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex410. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous