Division and Regrowth of Phase-Separated Giant Unilamellar Vesicles*
- PMID: 33355974
- PMCID: PMC8252472
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202014174
Division and Regrowth of Phase-Separated Giant Unilamellar Vesicles*
Abstract
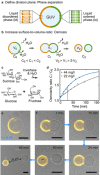
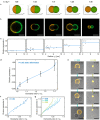
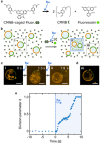
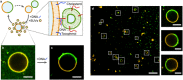
Success in the bottom-up assembly of synthetic cells will depend on strategies for the division of protocellular compartments. Here, we describe the controlled division of phase-separated giant unilamellar lipid vesicles (GUVs). We derive an analytical model based on the vesicle geometry, which makes four quantitative predictions that we verify experimentally. We find that the osmolarity ratio required for division is , independent of the GUV size, while asymmetric division happens at lower osmolarity ratios. Remarkably, we show that a suitable osmolarity change can be triggered by water evaporation, enzymatic decomposition of sucrose or light-triggered uncaging of CMNB-fluorescein. The latter provides full spatiotemporal control, such that a target GUV undergoes division whereas the surrounding GUVs remain unaffected. Finally, we grow phase-separated vesicles from single-phased vesicles by targeted fusion of the opposite lipid type with programmable DNA tags to enable subsequent division cycles.
Keywords: DNA structures; GUV division; osmosis; synthetic biology; vesicles.
© 2020 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Raspail F. V., Ann. Sci. Nat. 1825, 224, 384–427.
-
- Virchow R., Die Cellularpathologie in ihrer Begründung und in ihrer Auswirkung auf die physiologische und pathologische Gewebelehr e, Verlag A. Hirschwald, Berlin, 1858.
-
- Schwille P., Science 2011, 333, 1252–1254. - PubMed
-
- Schwille P., Emerging Top. Life Sci. 2019, 3, 551–558. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

