Molecular mechanisms of the disturbance caused by malondialdehyde on probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri PL503
- PMID: 33356002
- PMCID: PMC8867985
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13723
Molecular mechanisms of the disturbance caused by malondialdehyde on probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri PL503
Abstract
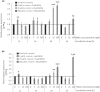
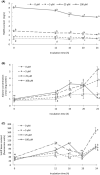
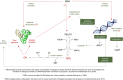
This study aimed to provide insight into the molecular and genetic mechanisms implicated in the responses of Lactobacillus reuteri against the oxidative stress induced by malondialdehyde (MDA) by analysing protein oxidation and assessing the uspA and the dhaT genes. Four experimental groups were evaluated depending on the concentration of MDA added in Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) broth: Control (L. reuteri), 5 µM (L. reuteri + 5 µM MDA), 25 µM (L. reuteri + 25 µM MDA) and 100 µM (L. reuteri + 100 µM MDA). Three replicates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in microaerophilic conditions and sampled at 12, 16, 20 and 24 h. The upregulation of the uspA gene by L. reuteri indicates the recognition of MDA as a potential DNA-damaging agent. The dhaT gene, encoding a NADH-dependent-oxidoreductase, was also upregulated at the highest MDA concentrations. This gene was proposed to play a role in the antioxidant response of L. reuteri. The incubation of L. reuteri with MDA increased the production of ROS and caused thiol depletion and protein carbonylation. L. reuteri is proposed to detoxify pro-oxidative species while the underlying mechanism requires further elucidation.
© 2020 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arcanjo, N.O. , Andrade, M.J. , Padilla, P. , Rodríguez, A. , Madruga, M.S. , and Estévez, M. (2019) Resveratrol protects Lactobacillus reuteri against H2O2 – induced oxidative stress and stimulates antioxidant defenses through upregulation of the dhaT gene. Free Radic Biol Med 135: 38–45. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.02.023 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

