Location and Conformation of the LKα14 Peptide in Water/Ethanol Mixtures
- PMID: 33356282
- PMCID: PMC7871320
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03132
Location and Conformation of the LKα14 Peptide in Water/Ethanol Mixtures
Abstract
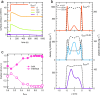
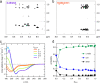
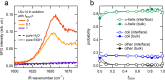
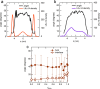
It is widely recognized that solvation is one of the major factors determining structure and functionality of proteins and long peptides, however it is a formidable challenge to address it both experimentally and computationally. For this reason, simple peptides are used to study fundamental aspects of solvation. It is well established that alcohols can change the peptide conformation and tuning of the alcohol content in solution can dramatically affect folding and, as a consequence, the function of the peptide. In this work, we focus on the leucine and lysine based LKα14 peptide designed to adopt an α-helical conformation at an apolar-polar interface. We investigate LKα14 peptide's bulk and interfacial behavior in water/ethanol mixtures combining a suite of experimental techniques (namely, circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for the bulk solution, surface pressure measurements and vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy for the air-solution interface) with molecular dynamics simulations. We observe that ethanol highly affects both the peptide location and conformation. At low ethanol content LKα14 lacks a clear secondary structure in bulk and shows a clear preference to reside at the air-solution interface. When the ethanol content in solution increases, the peptide's interfacial affinity is markedly reduced and the peptide approaches a stable α-helical conformation in bulk facilitated by the amphiphilic nature of the ethanol molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conformation and Aggregation of LKα14 Peptide in Bulk Water and at the Air/Water Interface.J Phys Chem B. 2015 Dec 10;119(49):15164-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b08871. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Phys Chem B. 2015. PMID: 26551581
-
Solid state deuterium NMR study of LKα14 peptide aggregation in biosilica.Biointerphases. 2017 Jun 27;12(2):02D418. doi: 10.1116/1.4986907. Biointerphases. 2017. PMID: 28655279 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Design and Characterization of Amphiphilic Peptides with Basic Side Chains for Tailored Interfacial Chemistries.Langmuir. 2024 Sep 17;40(37):19404-19411. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01654. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39213639
-
Visualization of the Orientation of Amphipathic Peptides at the Air-Water Interface by X-Ray Reflectometry.Anal Sci. 2021 Nov 10;37(11):1505-1509. doi: 10.2116/analsci.21P068. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Anal Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867403
-
Engineering and Characterization of Peptides and Proteins at Surfaces and Interfaces: A Case Study in Surface-Sensitive Vibrational Spectroscopy.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Jun 21;49(6):1149-57. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00091. Epub 2016 May 18. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27188920 Review.
Cited by
-
Choosing an Optimal Solvent Is Crucial for Obtaining Cell-Penetrating Peptide Nanoparticles with Desired Properties and High Activity in Nucleic Acid Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 24;15(2):396. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020396. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839718 Free PMC article.
-
Spidroins under the Influence of Alcohol: Effect of Ethanol on Secondary Structure and Molecular Level Solvation of Silk-Like Proteins.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Dec 11;24(12):5638-5653. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00637. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 38019577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kinoshita M.; Okamoto Y.; Hirata F. Peptide Conformations in Alcohol and Water: Analyses by the Reference Interaction Site Model Theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122 (12), 2773–2779. 10.1021/ja993939x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

