Epigenetic targeting of Waldenström macroglobulinemia cells with BET inhibitors synergizes with BCL2 or histone deacetylase inhibition
- PMID: 33356554
- PMCID: PMC8656319
- DOI: 10.2217/epi-2020-0189
Epigenetic targeting of Waldenström macroglobulinemia cells with BET inhibitors synergizes with BCL2 or histone deacetylase inhibition
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Epigenomics. 2021 Jun;13(11):909-911. doi: 10.2217/epi-2020-0189c1. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Epigenomics. 2021. PMID: 33899492 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
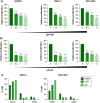
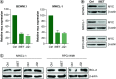
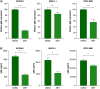
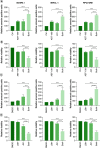
Aim: Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a low-grade B-cell lymphoma characterized by overproduction of monoclonal IgM. To date, there are no therapies that provide a cure for WM patients, and therefore, it is important to explore new therapies. Little is known about the efficiency of epigenetic targeting in WM. Materials & methods: WM cells were treated with BET inhibitors (JQ1 and I-BET-762) and venetoclax, panobinostat or ibrutinib. Results: BET inhibition reduces growth of WM cells, with little effect on survival. This finding was enhanced by combination therapy, with panobinostat (LBH589) showing the highest synergy. Conclusion: Our studies identify BET inhibitors as effective therapy for WM, and these inhibitors can be enhanced in combination with BCL2 or histone deacetylase inhibition.
Keywords: BET inhibitors; Waldenström macroglobulinemia; epigenetics; panobinostat; venetoclax.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was supported by an NIH COBRE Center of Integrated Biomedical and Bioengineering Research (CIBBR, P20 GM113131) through an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. This work was supported in part by a grant from the International Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Foundation and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (IWMF-LLS). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Kapoor P, Paludo J, Vallumsetla N, Greipp PR. Waldenström macroglobulinemia: what a hematologist needs to know. Blood Rev. 29(5), 301–319 (2015). - PubMed
-
•• Discusses aspects of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) disease.
-
- Treon SP, Gustine J, Meid K et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, treatment-naïve patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 36(27), 2755–2761 (2018). - PubMed
-
• Discusses the role of ibrutinib in WM.
-
- Sun JY, Xu L, Tseng H et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors demonstrate significant preclinical activity as single agents, and in combination with bortezomib in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 11, 152-156 (2011). - PubMed
-
• Efficacy of epigenetic targeting in WM using histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
