Evaluation of dietary supplement, functional food and herbal medicine use by dietitians during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33357253
- PMCID: PMC7853745
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980020005297
Evaluation of dietary supplement, functional food and herbal medicine use by dietitians during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Objective: The current study was conducted to evaluate the dietary habits of the dietitians who had a leading role in this regard during the pandemic and their use of dietary supplements, functional food and herbal medicines.
Design: A cross-sectional study. An online questionnaire was used as a data collection tool to identify the participants’ socio-demographic characteristics, health statuses and dietary habits and their use of dietary supplements, functional foods and herbal medicines.
Setting: Turkey.
Participants: The study population was 550 dietitians.
Results: In the current study, the participants’ average age was 30·6 ± 9·1 years, and most of them (88·2 %) were women. More than half of the participants (88·9 %) thought that adequate and balanced nutrition would positively affect the course of COVID-19. To avoid COVID-19, 94·5 % of the dietitians used dietary supplements, 46·1 % herbal medicines and 34·9 % functional foods during the pandemic. The most commonly used dietary supplement was fish oil (81·9 %), functional food was vegetables and fruits (80·5 %) and the herbal medicine was cinnamon (63·5 %). Women’s consumption of functional foods was approximately twice higher compared with men (95 % Cl: 1·048, 4·165; P < 0·05). The findings showed that the longer the dietitians were in their careers, the more functional foods and herbal medicines they used.
Conclusion: During the pandemic, dietitians’ use of foods with protective effects against diseases increased depending on their academic knowledge and experience in nutrition. The findings obtained in the current study suggest that an expert’s opinion should be obtained before using dietary supplements and herbal medicines.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dietary supplements; Dietitians; Functional foods; Herbal medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Republic of Turkey Ministry of Health (2020) What is COVID-19 (New Coronavirus Disease)? https://covid19bilgi.saglik.gov.tr/tr/covid-19-yeni-koronavirus-hastalig... (accessed June 2020).
-
- Tosh PK (2020) Coronavirus: what is it and how can I protect myself? https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/expert-answer... (accessed June 2020).
-
- Unicef (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): What is it really? https://www.unicef.org/wca/what-is-coronavirus (accessed June 2020).
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://www.who.int (accessed September 2020).
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1 (accessed June 2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

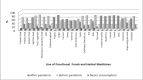
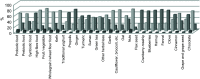
 , after pandemic;
, after pandemic;  , before pandemic;
, before pandemic;  …
… 