[Clinical Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid ctDNA in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Meningeal Metastasis]
- PMID: 33357310
- PMCID: PMC7786234
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.102.42
[Clinical Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid ctDNA in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Meningeal Metastasis]
Abstract
Background: The mortality rate of lung cancer meningeal metastasis is extremely high. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has been confirmed to be contain the genomic alterations present in tumors and has been used to monitor tumor progression and response to treatments. Due to the presence of blood-brain barrier and other factors, peripheral blood ctDNA cannot reflect the information of brain lesions for patients with meningeal metastases. However, cerebrospinal fluid ctDNA as a test sample can better reflect the genetic status of intracranial tumors and guide clinical targeted treatment of intracranial lesions. This study explored the feasibility of cerebrospinal fluid ctNDA for evaluating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) meningeal metastasis and the potential clinical value of cerebrospinal fluid ctDNA detection in NSCLC meningeal metastasis.
Methods: A total of 21 patients with NSCLC meningeal metastasis were included. Tumor genomic variation was performed on the cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood samples of patients by second-generation gene sequencing technology. The situation was examined, and pathological evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid cytology and head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enhanced examination were performed.
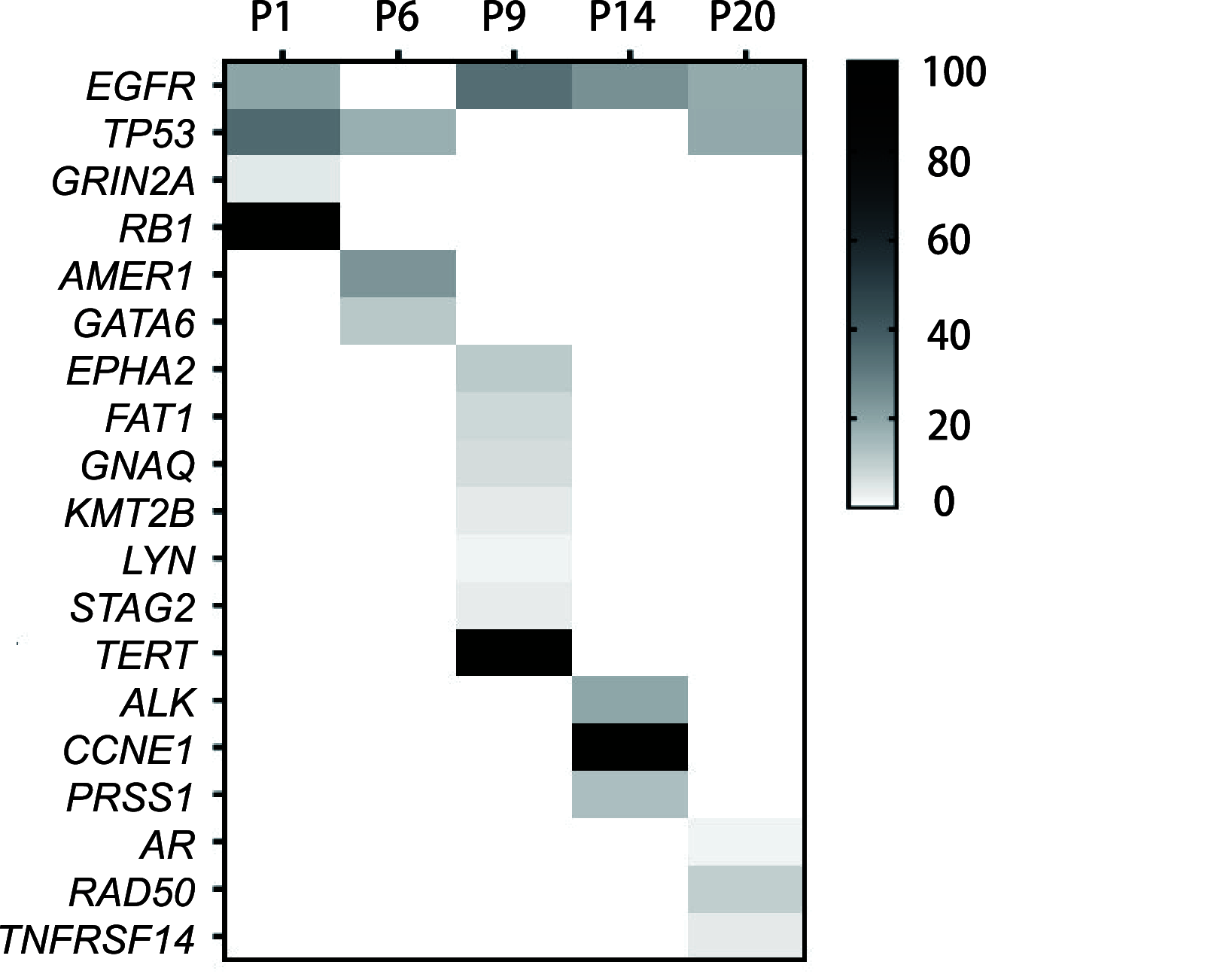
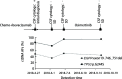
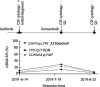
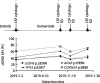
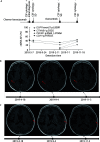
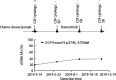
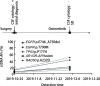
Results: ctDNA was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of 21 patients. The sensitivity of cerebrospinal fluid ctDNA detection was superior to cytology in the diagnosis of meningeal metastasis (P<0.001). The detection rate and gene mutation abundance of cerebrospinal fluid were higher than plasma (P<0.001). Cerebro-spinal fluid had a unique genetic profile. In 6 patients with dynamic detection, changes of ctDNA allele fraction occurred at the same time or earlier than clinical disease changes, which could timely monitor drug resistance mechanism and relapse trend.
Conclusions: The detection rate of ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid is higher than that in cytology and imaging. The detection of ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid can reveal the specific mutation map of meningeal metastasis lesions. The dynamic monitoring of ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid has hint significance for clinical response of lung cancer patients.
【中文题目:脑脊液ctDNA对非小细胞肺癌脑膜转移患者的临床价值】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 肺癌脑膜转移病死率极高。循环肿瘤DNA(circulating tumor DNA, ctDNA)已被证实含有肿瘤的基因组改变信息,并已被用于监测肿瘤的进展和对治疗的响应。对于存在脑膜转移瘤的患者,由于血脑屏障等因素的存在,外周血ctDNA不能反映脑部病灶的信息,此时脑脊液ctDNA作为检测样本能更好地体现颅内肿瘤的基因状态,指导临床对颅内病灶的靶向治疗。本研究旨在探究脑脊液ctNDA用于监测非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)脑膜转移的可行性以及脑脊液ctDNA检测对NSCLC脑膜转移的临床价值。方法 入组NSCLC脑膜转移患者21例,通过二代基因测序技术对患者的脑脊液及外周血样本进行基因检测,并进行脑脊液细胞学病理学检测和头颅核磁共振增强检查。结果 入组21例患者脑脊液中均检测到ctDNA。脑脊液ctDNA检测的灵敏性在脑膜转移诊断方面优于细胞学(P<0.001)。脑脊液的基因突变检出率及基因突变丰度均高于血浆(P<0.001)。脑脊液具有独特的基因谱。6例动态检测的患者中,脑脊液中ctDNA丰度变化均同时或早于临床疾病变化出现,可及时揭示耐药机制和监测复发趋势。结论 脑脊液ctDNA检出率高于细胞学及影像学;脑脊液ctDNA检测可展现脑膜转移病灶特有的突变图谱;脑脊液ctDNA动态监测对肺癌患者临床疗效具有提示意义。 】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;脑膜转移;循环肿瘤DNA;疗效评价】.
Keywords: Circulating tumor DNA; Lung neoplasms; Meningeal metastasis; Response evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
【
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

