Functional implications of MIR domains in protein O-mannosylation
- PMID: 33357379
- PMCID: PMC7759382
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.61189
Functional implications of MIR domains in protein O-mannosylation
Abstract
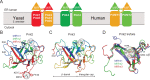
Protein O-mannosyltransferases (PMTs) represent a conserved family of multispanning endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins involved in glycosylation of S/T-rich protein substrates and unfolded proteins. PMTs work as dimers and contain a luminal MIR domain with a β-trefoil fold, which is susceptive for missense mutations causing α-dystroglycanopathies in humans. Here, we analyze PMT-MIR domains by an integrated structural biology approach using X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy and evaluate their role in PMT function in vivo. We determine Pmt2- and Pmt3-MIR domain structures and identify two conserved mannose-binding sites, which are consistent with general β-trefoil carbohydrate-binding sites (α, β), and also a unique PMT2-subfamily exposed FKR motif. We show that conserved residues in site α influence enzyme processivity of the Pmt1-Pmt2 heterodimer in vivo. Integration of the data into the context of a Pmt1-Pmt2 structure and comparison with homologous β-trefoil - carbohydrate complexes allows for a functional description of MIR domains in protein O-mannosylation.
Keywords: NMR; S. cerevisiae; carbohydrate-binding module; enzymatic processivity; glycosyltransferase; molecular biophysics; protein O-mannosylation; structural biology; x-ray crystallography.
© 2020, Chiapparino et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AC, AG, HJ, YH, SM, EZ, AS, GS, KS, KW, HS, SS, IS No competing interests declared
Figures
















References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FOR2509 SI586/8-1/German Research Foundation/International
- 201348542-SFB1036 TP11/German Research Foundation/International
- FOR2509 STR443/5-1/German Research Foundation/International
- FOR2509 SCHW701/20-1/German Research Foundation/International
- Leibniz Program SI586/6-1/German Research Foundation/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

