Gender differences in the epidemiology of Rheumatic Fever/Rheumatic heart disease (RF/RHD) patient population of hill state of northern India; 9 years prospective hospital based, HP-RHD registry
- PMID: 33357644
- PMCID: PMC7772586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2020.09.011
Gender differences in the epidemiology of Rheumatic Fever/Rheumatic heart disease (RF/RHD) patient population of hill state of northern India; 9 years prospective hospital based, HP-RHD registry
Abstract
Objectives: We report the gender-based differences in the prevalence, severity, pattern of valvular involvement, and complications in patients with Rheumatic Fever/Rheumatic heart disease (RF/RHD).
Methods: The 2475 consecutive patients with RF/RHD diagnosed using clinical and echocardiographic criteria were registered prospectively from January 2011 till December 2019. The association of gender with the pattern of valvular involvement, nature, and severity of valvular dysfunction and cardiovascular complications was analyzed using a logistic regression model, and odds ratios with 95% CI were estimated.
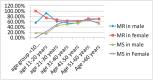
Results: The mitral and tricuspid valve involvement was significantly lower in the male gender, odds ratio with 95% CI of 0.55 (0.44-0.61), and 0.69 (0.58-0.83) respectively, while the aortic valve was affected more frequently than females, odds ratio 1.36 (1.14-1.62). The severity of valvular disease had no significant association with gender, 0.99 (0.82-1.20). The association between gender and cardiovascular complications, heart failure, stroke, and atrial fibrillations were not statistically significant. The prevalence of RF/RHD was more than two-fold higher in female gender than male (71.4% vs. 29.6%, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: RF/RHD is more prevalent in females. Gender has a significant association with the pattern of valvular involvement. The severity of valvular dysfunction and cardiovascular complications had no significant association with gender.
Keywords: Adverse cardiovascular events; Epidemiology; Gender; Prevalence; Rheumatic fever; Rheumatic heart diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors have none to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Lozano R., Naghavi M., Foreman K. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–2128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. [published correction appears in Lancet. 2013 Feb 23;381(9867):628. AlMazroa, Mohammad A [added]; Memish, Ziad A [added]] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous