Autoantibodies as Endogenous Modulators of GPCR Signaling
- PMID: 33358695
- PMCID: PMC7880908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2020.11.013
Autoantibodies as Endogenous Modulators of GPCR Signaling
Abstract
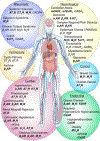
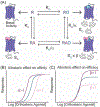
Endogenous self-reactive autoantibodies (AAs) recognize a range of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). They are frequently associated with cardiovascular, neurological, and autoimmune disorders, and in some cases directly impact disease progression. Many GPCR AAs modulate receptor signaling, but molecular details of their modulatory activity are not well understood. Technological advances have provided insight into GPCR biology, which now facilitates deeper understanding of GPCR AA function at the molecular level. Most GPCR AAs are allosteric modulators and exhibit a broad range of pharmacological properties, altering both receptor signaling and trafficking. Understanding GPCR AAs is not only important for defining how these unusual GPCR modulators function in disease, but also provides insight into the potential use and limitations of using therapeutic antibodies to modulate GPCR signaling.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor; allosteric modulation; autoantibody; autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Rodgers KR and Chou RC (2016) Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and derivatives: Historical perspectives and future directions. Biotechnol Adv 34 (6), 1149–1158. - PubMed
-
- Hutchings CJ et al. (2017) Opportunities for therapeutic antibodies directed at G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16 (9), 661. - PubMed
-
- Hutchings CJ (2020) A review of antibody-based therapeutics targeting G protein-coupled receptors: an update. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

