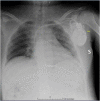
Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in post-mortem swab 35 days after death: A case report
- PMID: 33360242
- PMCID: PMC7725267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2020.110653
Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in post-mortem swab 35 days after death: A case report
Abstract
Post-mortem swabs for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA detection have been recommended by several Scientific Committees and Institutions as a standard procedure for post-mortem assessment of potential Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) related deaths. To date there is no data about the SARS-CoV-2 RNA detectability period in human bodies after death. The present case documents the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the upper respiratory tract 35-days after death. Post-mortem swabs could be used as a valuable tool in preventive evaluation of the risks-benefits ratio associated with autopsy execution. SARS-CoV-2 RNA post-mortem detection could have a key diagnostic role in deaths lacking medical assistance, unattended deaths, and patients with multiple comorbidities. Based on the present report, staged post-mortem swabs should be performed even after a long post-mortem interval.
Keywords: Autopsy; Biosafety; COVID-19; Post-mortem diagnosis; Post-mortem swab; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . 2020. World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease Situation Report - 118.
-
- Nihan Z., et al. Investigation of viral respiratory tract infection agents by multiplex PCR method in autopsy cases: a five-year study. Mikrobiyoloji bülteni. 2019;53(April (2)):179–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous