Value of minimum intensity projections for chest CT in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33360269
- PMCID: PMC7831963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109478
Value of minimum intensity projections for chest CT in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
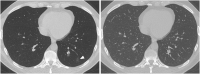
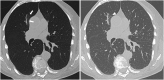
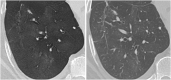
Purpose: To investigate whether minimum intensity projection (MinIP) reconstructions enable more accurate depiction of pulmonary ground-glass opacity (GGO) compared to standard transverse sections and multiplanar reformat (MPR) series in patients with suspected coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Method: In this multinational study, chest CT scans of 185 patients were retrospectively analyzed. Diagnostic accuracy, diagnostic confidence, image quality regarding the assessment of GGO, as well as subjective time-efficiency of MinIP and standard MPR series were analyzed based on the assessment of six radiologists. In addition, the suitability for COVID-19 evaluation, image quality regarding GGO and subjective time-efficiency in clinical routine was assessed by five clinicians.
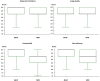
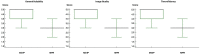
Results: The reference standard revealed a total of 149 CT scans with pulmonary GGO. MinIP reconstructions yielded significantly higher sensitivity (99.9 % vs 95.6 %), specificity (95.8 % vs 86.1 %) and accuracy (99.1 % vs 93.8 %) for assessing of GGO compared with standard MPR series. MinIP reconstructions achieved significantly higher ratings by radiologists concerning diagnostic confidence (medians, 5.00 vs 4.00), image quality (medians, 4.00 vs 4.00), contrast between GGO and unaffected lung parenchyma (medians, 5.00 vs 4.00) as well as subjective time-efficiency (medians, 5.00 vs 4.00) compared with MPR-series (all P < .001). Clinicians preferred MinIP reconstructions for COVID-19 assessment (medians, 5.00 vs 3.00), image quality regarding GGO (medians, 5.00 vs 3.00) and subjective time-efficiency in clinical routine (medians, 5.00 vs 3.00).
Conclusions: MinIP reconstructions improve the assessment of COVID-19 in chest CT compared to standard images and may be suitable for routine application.
Keywords: COVID-19; Multidetector computed tomography; Pneumonia; Spiral computed; Tomography; Viral infection.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
C.B. has received speaker fees from Siemens Healthineers. U.J.S. has received institutional research support, consulting fees, and/or speaker honoraria from Bayer, Bracco, Elucid BioImaging, GE, Guerbet, HeartFlow Inc., Keya Medical, and Siemens Healthineers. I.Y. has received a speaker fee from Siemens Healthineers. M.H.A. has received speaker fees from Siemens Healthineers and Bracco. The other authors have no potential conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Organization W.H . Situation Report; 2020. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) p. 51.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

