Dissemination of child abuse clinical decision support: Moving beyond a single electronic health record
- PMID: 33360791
- PMCID: PMC8351590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104349
Dissemination of child abuse clinical decision support: Moving beyond a single electronic health record
Abstract
Background: Child maltreatment is a leading cause of pediatric morbidity and mortality. We previously reported on development and implementation of a child abuse clinical decision support system (CA-CDSS) in the Cerner electronic health record (EHR). Our objective was to develop a CA-CDSS in two different EHRs.
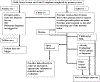
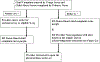
Methods: Using the CA-CDSS in Cerner as a template, CA-CDSSs were developed for use in four hospitals in the Northwell Health system who use Allscripts and two hospitals in the University of Wisconsin health system who use Epic. Each system had a combination of triggers, alerts and child abuse-specific order sets. Usability evaluation was done prior to launch of the CA-CDSS.
Results: Over an 18-month period, a CA-CDSS was embedded into Epic and Allscripts at two hospital systems. The CA-CDSSs vary significantly from each other in terms of the type of triggers which were able to be used, the type of alert, the ability of the alert to link directly to child abuse-specific order sets and the order sets themselves.
Conclusions: Dissemination of CA-CDSS from one EHR into the EHR in other health care systems is possible but time-consuming and needs to be adapted to the strengths and limitations of the specific EHR. Site-specific usability evaluation, buy-in of multiple stakeholder groups and significant information technology support are needed. These barriers limit scalability and widespread dissemination of CA-CDSS.
Keywords: Child abuse; Child maltreatment; Clinical decision support; Electronic health record; Physical abuse.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


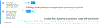







References
-
- Child Maltreatment 2018. Washington D.C.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau; 2020.
-
- Centers for Disease Control. 10 Leading Causes of Death by Age Group, United States - 2018 2018. [Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_by_a....
-
- Jenny C, Hymel KP, Ritzen A, Reinert SE, Hay TC. Analysis of missed cases of abusive head trauma. JAMA. 1999;281(7):621–6. - PubMed
-
- Ravichandiran N, Schuh S, Bejuk M, Al-Harthy N, Shouldice M, Au H, et al. Delayed identification of pediatric abuse-related fractures. Pediatrics. 2010;125(1):60–6. - PubMed
-
- King WK, Kiesel EL, Simon HK. Child abuse fatalities: are we missing opportunities for intervention? Pediatric emergency care. 2006;22(4):211–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

