Early use of nitazoxanide in mild COVID-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 33361100
- PMCID: PMC7758778
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.03725-2020
Early use of nitazoxanide in mild COVID-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Nitazoxanide is widely available and exerts broad-spectrum antiviral activity in vitro. However, there is no evidence of its impact on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection.
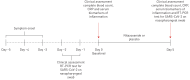
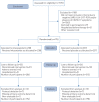
Methods: In a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adult patients presenting up to 3 days after onset of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms (dry cough, fever and/or fatigue) were enrolled. After confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection using reverse transcriptase PCR on a nasopharyngeal swab, patients were randomised 1:1 to receive either nitazoxanide (500 mg) or placebo, three times daily, for 5 days. The primary outcome was complete resolution of symptoms. Secondary outcomes were viral load, laboratory tests, serum biomarkers of inflammation and hospitalisation rate. Adverse events were also assessed.
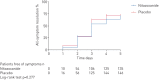
Results: From June 8 to August 20, 2020, 1575 patients were screened. Of these, 392 (198 placebo, 194 nitazoxanide) were analysed. Median (interquartile range) time from symptom onset to first dose of study drug was 5 (4-5) days. At the 5-day study visit, symptom resolution did not differ between the nitazoxanide and placebo arms. Swabs collected were negative for SARS-CoV-2 in 29.9% of patients in the nitazoxanide arm versus 18.2% in the placebo arm (p=0.009). Viral load was reduced after nitazoxanide compared to placebo (p=0.006). The percentage viral load reduction from onset to end of therapy was higher with nitazoxanide (55%) than placebo (45%) (p=0.013). Other secondary outcomes were not significantly different. No serious adverse events were observed.
Conclusions: In patients with mild COVID-19, symptom resolution did not differ between nitazoxanide and placebo groups after 5 days of therapy. However, early nitazoxanide therapy was safe and reduced viral load significantly.
Copyright ©ERS 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: P.R.M. Rocco reports personal fees for data monitoring committee work from Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: P.L. Silva has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: F.F. Cruz has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.A.C.M. Junior has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P.F.G.M.M. Tierno has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.A. Moura has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: L.F.G. De Oliveira has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C.C. Lima has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E.A. Dos Santos has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: W.F. Junior has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.P.S.M. Fernandes has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: K.G. Franchini has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Magri has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N.F. de Moraes has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J.M.J Gonçalves has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.N. Carbonieri has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: I.S. Dos Santos has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N.F. Paes has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P.V.M. Maciel has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R.P. Rocha has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.F. de Carvalho has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P.A. Alves has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J.L.P. Modena has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.T. Cordeiro has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D.B.B. Trivella has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R.E. Marques has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R.R. Luiz has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P. Pelosi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J.R. Lapa e Silva has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
