Afucosylated IgG characterizes enveloped viral responses and correlates with COVID-19 severity
- PMID: 33361116
- PMCID: PMC7919849
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abc8378
Afucosylated IgG characterizes enveloped viral responses and correlates with COVID-19 severity
Abstract
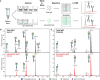
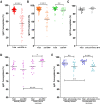
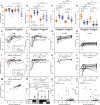
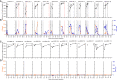
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are crucial for protection against invading pathogens. A highly conserved N-linked glycan within the IgG-Fc tail, which is essential for IgG function, shows variable composition in humans. Afucosylated IgG variants are already used in anticancer therapeutic antibodies for their increased activity through Fc receptors (FcγRIIIa). Here, we report that afucosylated IgG (approximately 6% of total IgG in humans) are specifically formed against enveloped viruses but generally not against other antigens. This mediates stronger FcγRIIIa responses but also amplifies brewing cytokine storms and immune-mediated pathologies. Critically ill COVID-19 patients, but not those with mild symptoms, had high concentrations of afucosylated IgG antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), amplifying proinflammatory cytokine release and acute phase responses. Thus, antibody glycosylation plays a critical role in immune responses to enveloped viruses, including COVID-19.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

References
-
- Shields R. L., Lai J., Keck R., O’Connell L. Y., Hong K., Meng Y. G., Weikert S. H. A., Presta L. G., Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fcgamma RIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 26733–26740 (2002). 10.1074/jbc.M202069200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

