Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33361145
- PMCID: PMC7896255
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-2219
Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Objective: Real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) in critically ill hospitalized patients holds promise; however, real-world data are needed.
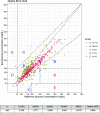
Research design and methods: We placed Dexcom G6 CGM on intensive care unit (ICU) patients at Montefiore Medical Center with confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection and glycemic variability. We analyzed inpatient CGM accuracy using point-of-care (POC) glucose-CGM matched pairs and included patients for analysis regardless of clinical status.
Results: We included 11 patients with CGM: 8 on continuous insulin infusion (CII), 8 on vasopressors, 8 intubated, 4 on high-dose glucocorticoids, 6 on renal replacement therapy, and 2 with anasarca. Accuracy was 12.58% for mean and 6.3% for median absolute relative difference. CGM reduced POC testing by ∼60% for patients on CII.
Conclusions: In this real-world preliminary analysis of rtCGM during critical illness, we demonstrate early feasibility, considerable accuracy, and meaningful reduction in the frequency of POC glucose testing.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Ushigome E, Yamazaki M, Hamaguchi M, et al. Usefulness and safety of remote continuous glucose monitoring for a severe COVID-19 patient with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2021;23:78–80 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous