Discordant neutralizing antibody and T cell responses in asymptomatic and mild SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33361161
- PMCID: PMC8101131
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf3698
Discordant neutralizing antibody and T cell responses in asymptomatic and mild SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
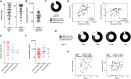
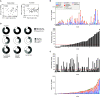
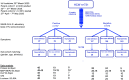
Understanding the nature of immunity following mild/asymptomatic infection with SARS-CoV-2 is crucial to controlling the pandemic. We analyzed T cell and neutralizing antibody responses in 136 healthcare workers (HCW) 16-18 weeks after United Kingdom lockdown, 76 of whom had mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection captured by serial sampling. Neutralizing antibodies (nAb) were present in 89% of previously infected HCW. T cell responses tended to be lower following asymptomatic infection than in those reporting case-definition symptoms of COVID-19, while nAb titers were maintained irrespective of symptoms. T cell and antibody responses were sometimes discordant. Eleven percent lacked nAb and had undetectable T cell responses to spike protein but had T cells reactive with other SARS-CoV-2 antigens. Our findings suggest that the majority of individuals with mild or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection carry nAb complemented by multispecific T cell responses at 16-18 weeks after mild or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


References
-
- Ni L., Ye F., Cheng M. L., Feng Y., Deng Y. Q., Zhao H., Wei P., Ge J., Gou M., Li X., Sun L., Cao T., Wang P., Zhou C., Zhang R., Liang P., Guo H., Wang X., Qin C. F., Chen F., Dong C., Detection of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immunity in COVID-19 Convalescent Individuals. Immunity 52, 971–977.e3 (2020). 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.023 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grifoni A., Weiskopf D., Ramirez S. I., Mateus J., Dan J. M., Moderbacher C. R., Rawlings S. A., Sutherland A., Premkumar L., Jadi R. S., Marrama D., de Silva A. M., Frazier A., Carlin A. F., Greenbaum J. A., Peters B., Krammer F., Smith D. M., Crotty S., Sette A., Targets of T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus in Humans with COVID-19 Disease and Unexposed Individuals. Cell 181, 1489–1501.e15 (2020). 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le Bert N., Tan A. T., Kunasegaran K., Tham C. Y. L., Hafezi M., Chia A., Chng M. H. Y., Lin M., Tan N., Linster M., Chia W. N., Chen M. I., Wang L. F., Ooi E. E., Kalimuddin S., Tambyah P. A., Low J. G., Tan Y. J., Bertoletti A., SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls. Nature 584, 457–462 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2550-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peng Y., Mentzer A. J., Liu G., Yao X., Yin Z., Dong D., Dejnirattisai W., Rostron T., Supasa P., Liu C., López-Camacho C., Slon-Campos J., Zhao Y., Stuart D. I., Paesen G. C., Grimes J. M., Antson A. A., Bayfield O. W., Hawkins D. E. D. P., Ker D. S., Wang B., Turtle L., Subramaniam K., Thomson P., Zhang P., Dold C., Ratcliff J., Simmonds P., de Silva T., Sopp P., Wellington D., Rajapaksa U., Chen Y. L., Salio M., Napolitani G., Paes W., Borrow P., Kessler B. M., Fry J. W., Schwabe N. F., Semple M. G., Baillie J. K., Moore S. C., Openshaw P. J. M., Ansari M. A., Dunachie S., Barnes E., Frater J., Kerr G., Goulder P., Lockett T., Levin R., Zhang Y., Jing R., Ho L. P., Cornall R. J., Conlon C. P., Klenerman P., Screaton G. R., Mongkolsapaya J., McMichael A., Knight J. C., Ogg G., Dong T.; Oxford Immunology Network Covid-19 Response T cell Consortium; ISARIC4C Investigators , Broad and strong memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 in UK convalescent individuals following COVID-19. Nat. Immunol. 21, 1336–1345 (2020). 10.1038/s41590-020-0782-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thieme C. J., Anft M., Paniskaki K., Blazquez-Navarro A., Doevelaar A., Seibert F. S., Hoelzer B., Konik M. J., Berger M. M., Brenner T., Tempfer C., Watzl C., Meister T. L., Pfaender S., Steinmann E., Dolff S., Dittmer U., Westhoff T. H., Witzke O., Stervbo U., Roch T., Babel N., Robust T Cell Response Toward Spike, Membrane, and Nucleocapsid SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Is Not Associated with Recovery in Critical COVID-19 Patients. Cell Rep Med 1, 100092 (2020). 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

