Cross-Border Emergence of Escherichia coli Producing the Carbapenemase NDM-5 in Switzerland and Germany
- PMID: 33361340
- PMCID: PMC8106709
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02238-20
Cross-Border Emergence of Escherichia coli Producing the Carbapenemase NDM-5 in Switzerland and Germany
Abstract
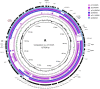
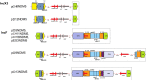
A series of clinical NDM-5-producing Escherichia coli isolates obtained from two surveillance networks for carbapenem-producing Enterobacterales from 2018 to 2019, namely, Switzerland (NARA) and Germany (SurvCARE), were analyzed. The 33 NDM-5-producing E. coli isolates were highly resistant to β-lactams, including novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations (ceftazidime-avibactam, imipenem-relebactam, and meropenem-vaborbactam), and remained susceptible to fosfomycin, colistin, and tigecycline. These isolates were assigned to different sequence types (STs) and indicated a predominance of isolates exhibiting ST167 in Switzerland and Germany (n = 10) (phylogenetic group C), followed by ST405 (n = 4) (phylogenetic group E), ST1284 (n = 4) (phylogenetic group C), and ST361 (n = 4) (phylogenetic group C). The blaNDM-5 gene was predominantly present on an IncF-type plasmid (n = 29) and, to a lesser extent, on the narrow-host-range IncX3 plasmid (n = 4). Sequence analyses of eight NDM-5 plasmids indicated that NDM-5-encoding F-type plasmids varied in size between 86 and 132 kb. The two IncX3 plasmids pCH8NDM5 and pD12NDM5 were 46 and 45 kb in size, respectively. The highly conserved blaNDM-5 genetic surrounding structures (ΔISAba125-blaNDM-5-bleMBL-trpT-dsbD-IS26) of both the F-type and IncX3 plasmids suggested a common genetic origin. The emergence of the NDM-5 carbapenemase was evidenced in particular for the E. coli ST167 clone, which is a successful epidemic clone known to be associated with both multiresistance and virulence traits and is therefore of high public health concern. The occurrence of clonally related NDM-5-producing E. coli isolates in Switzerland and Germany further indicates the international spread of this multidrug-resistant superbug at least throughout Europe.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; NDM; NDM-5; ST167; WGS; plasmid replicon; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Kumarasamy KK, Toleman MA, Walsh TR, Bagaria J, Butt F, Balakrishnan R, Chaudhary U, Doumith M, Giske CG, Irfan S, Krishnan P, Kumar AV, Maharjan S, Mushtaq S, Noorie T, Paterson DL, Pearson A, Perry C, Pike R, Rao B, Ray U, Sarma JB, Sharma M, Sheridan E, Thirunarayan MA, Turton J, Upadhyay S, Warner M, Welfare W, Livermore DM, Woodford N. 2010. Emergence of a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: a molecular, biological, and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis 10:597–602. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70143-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

