Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Plasma Agonist Activity Correlates With Disease Activity in Progressive MS
- PMID: 33361385
- PMCID: PMC7768947
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000933
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Plasma Agonist Activity Correlates With Disease Activity in Progressive MS
Abstract
Objective: The relationship between serum aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonistic activity levels with disease severity, its modulation over the course of relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), and its regulation in progressive MS (PMS) are unknown. Here, we report the analysis of AHR agonistic activity levels in cross-sectional and longitudinal serum samples of patients with RRMS and PMS.
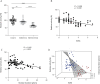
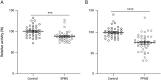
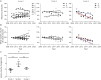
Methods: In a cross-sectional investigation, a total of 36 control patients diagnosed with noninflammatory diseases, 84 patients with RRMS, 35 patients with secondary progressive MS (SPMS), and 41 patients with primary progressive MS (PPMS) were included in this study. AHR activity was measured in a cell-based luciferase assay and correlated with age, sex, the presence of disease-modifying therapies, Expanded Disability Status Scale scores, and disease duration. In a second longitudinal investigation, we analyzed AHR activity in 13 patients diagnosed with RRMS over a period from 4 to 10 years and correlated AHR agonistic activity with white matter atrophy and lesion load volume changes.
Results: In RRMS, AHR ligand levels were globally decreased and associated with disease duration and neurologic disability. In SPMS and PPMS, serum AHR agonistic activity was decreased and correlated with disease severity. Finally, in longitudinal serum samples of patients with RRMS, decreased AHR agonistic activity was linked to progressive CNS atrophy and increased lesion load.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that serum AHR agonist levels negatively correlate with disability in RRMS and PMS and decrease longitudinally in correlation with MRI markers of disease progression. Thus, serum AHR agonistic activity may serve as novel biomarker for disability progression in MS.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
