The effect of adenosine triphosphate on propofol-induced myopathy in rats: a biochemical and histopathological evaluation
- PMID: 33361539
- PMCID: PMC7756530
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.1.69
The effect of adenosine triphosphate on propofol-induced myopathy in rats: a biochemical and histopathological evaluation
Abstract
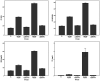
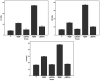
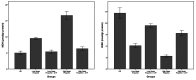
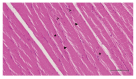
Propofol infusion syndrome characterized by rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, kidney, and heart failure has been reported in long-term propofol use for sedation. It has been reported that intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is reduced in rhabdomyolysis. The study aims to investigate the protective effect of ATP against possible skeletal muscle damage of propofol in albino Wistar male rats biochemically and histopathologically. PA-50 (n = 6) and PA-100 (n = 6) groups of animals was injected intraperitoneally to 4 mg/kg ATP. An equal volume (0.5 ml) of distilled water was administered intraperitoneally to the P-50, P-100, and HG groups. One hour after the administration of ATP and distilled water, 50 mg/kg propofol was injected intraperitoneally to the P-50 and PA-50 groups. This procedure was repeated once a day for 30 days. The dose of 100 mg/kg propofol was injected intraperitoneally to the P-100 and PA-100 groups. This procedure was performed three times with an interval of 1 days. Our experimental results showed that propofol increased serum CK, CK-MB, creatinine, BUN, TP I, ALT, AST levels, and muscle tissue MDA levels at 100 mg/kg compared to 50 mg/kg and decreased tGSH levels. At a dose of 100 mg/ kg, propofol caused more severe histopathological damage compared to 50 mg/ kg. It was found that ATP prevented propofol-induced muscle damage and organ dysfunction at a dose of 50 mg/kg at a higher level compared to 100 mg/kg. ATP may be useful in the treatment of propofol-induced rhabdomyolysis and multiple organ damage.
Keywords: Adenosine triphosphate; Muscle; Myopathy; Propofol; Rat; Rhabdomyolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of adenosine triphosphate on methylphenidate-induced oxidative and inflammatory kidney damage in rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2025 Jan 30:1-9. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2025.2457386. Online ahead of print. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39881661
-
Effects of adenosine triphosphate on methanol-induced experimental optic nerve damage in rats: biochemical and histopathological evaluation.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2020 Sep;39(3):244-248. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2020.1778017. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32543996
-
Effect of adenosine triphosphate, benidipine and their combinations on bevacizumab-induced kidney damage in rats.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021 Nov;30(11):1175-1183. doi: 10.17219/acem/140440. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34595851
-
[Propofol infusion syndrome].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2010 May;29(5):377-86. doi: 10.1016/j.annfar.2010.02.030. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2010. PMID: 20399595 Review. French.
-
Propofol-Related Infusion Syndrome: A Clinical Review.Cureus. 2022 Oct 17;14(10):e30383. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30383. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36407194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of adenosine triphosphate, thiamine pyrophosphate, melatonin, and liv-52 on subacute pyrazinamide proliferation hepatotoxicity in rats.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Mar 24;26(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00901-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40128909 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of adenosine triphosphate against cisplatin-induced necrotic and degenerative oral mucositis in rats.J Appl Oral Sci. 2025 Mar 24;33:e20250007. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2025-0007. eCollection 2025. J Appl Oral Sci. 2025. PMID: 40136224 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Adenosine Triphosphate against 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Oxidative Ovarian Damage in vivo.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Mar 1;24(3):1007-1013. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.3.1007. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 36974556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trevor AJ, Miller RD. General anesthetic. In: Katzung BG, editor. Basic and clinical pharmacology. 7th ed. Appleton & Lange; Stamford (CT): 1998. pp. 409–423.
-
- Secor T, Safadi AO, Gunderson S. Propofol toxicity. In: Gunderson S, editor. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): 2020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

