Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: from basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 33361764
- PMCID: PMC7758411
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00454-7
Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: from basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches
Abstract
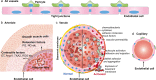
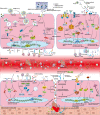
On 12 March 2020, the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization. As of 4 August 2020, more than 18 million confirmed infections had been reported globally. Most patients have mild symptoms, but some patients develop respiratory failure which is the leading cause of death among COVID-19 patients. Endothelial cells with high levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression are major participants and regulators of inflammatory reactions and coagulation. Accumulating evidence suggests that endothelial activation and dysfunction participate in COVID-19 pathogenesis by altering the integrity of vessel barrier, promoting pro-coagulative state, inducing endothelial inflammation, and even mediating leukocyte infiltration. This review describes the proposed cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial activation and dysfunction during COVID-19 emphasizing the principal mediators and therapeutic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. Update on 24:00 of August 04.
-
- [The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]. Zhonghua liu xing bing. xue za zhi.41, 145–151 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019M662543/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation/International
- 82002147/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 82073618/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 2018ZX10301407/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

