A proteomics-based method for identifying antigens within immune complexes
- PMID: 33362259
- PMCID: PMC7757895
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244157
A proteomics-based method for identifying antigens within immune complexes
Abstract
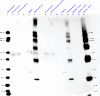
A novel approach to recover and identify immune complexes (ICs) was developed using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and affinity chromatography on immunoglobulin binding columns (HiTrap Protein G). The purification process was monitored by 1D SDS-PAGE, protein staining, Western blotting and, finally, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC MS/MS) was used to identify the recovered antigens. This approach was applied to serum with artificially created immune complexes (ICs) comprising vaccine antigen (influenza) and antibody, which led to recovery and identification of influenza peptides within the recovered ICs. This approach was compared with the established method for IC detection and recovery, polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation, followed by LC MS/MS. Both approaches successfully enabled capture, recovery and characterization of immunoglobulins and influenza antigen(s) in complex with the immunoglobulins. However, PEG precipitation has the advantage of simplicity and is more suited for large scale studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exists.
Figures



References
-
- Ronnelid J, Tejde A, Mathsson L, Nilsson-Ekdahl K, Nilsson B. Immune complexes from SLE sera induce IL10 production from normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells by an FcgammaRII dependent mechanism: implications for a possible vicious cycle maintaining B cell hyperactivity in SLE. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(1):37–42. Epub 2002/12/14. 10.1136/ard.62.1.37 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

