The contagion externality of a superspreading event: The Sturgis Motorcycle Rally and COVID-19
- PMID: 33362303
- PMCID: PMC7753804
- DOI: 10.1002/soej.12475
The contagion externality of a superspreading event: The Sturgis Motorcycle Rally and COVID-19
Abstract
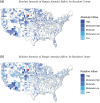
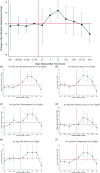
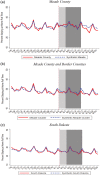
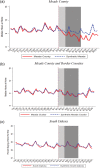
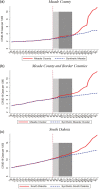
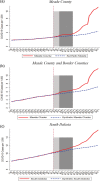
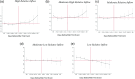
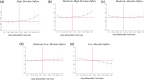
Large in-person gatherings of travelers who do not socially distance are classified as the "highest risk" for COVID-19 spread by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). From August 7-16, 2020, nearly 500,000 motorcycle enthusiasts converged on Sturgis, South Dakota for its annual rally in an environment without mask-wearing requirements or other mitigating policies. This study is the first to explore this event's public health impacts. First, using anonymized cell phone data, we document that foot traffic at restaurants/bars, retail establishments, and entertainment venues rose substantially at event locations. Stay-at-home behavior among local residents fell. Second, using a synthetic control approach, we find that the COVID-19 case rate increased substantially in Meade County and in the state of South Dakota in the month following the Rally. Finally, using a difference-in-differences model to assess nationwide spread, we find that following the Sturgis event, counties outside of South Dakota that contributed the highest inflows of rally attendees experienced a 6.4-12.5% increase in COVID-19 cases relative to counties without inflows. Our findings highlight that local policy decisions assessing the tradeoff between local economic benefits and COVID-19 health costs will not be socially optimal in the presence of large contagion externalities.
Keywords: COVID‐19; Sturgis Motorcycle Rally; large outdoor gathering; social distancing.
© 2020 The Southern Economic Association.
Figures
References
-
- Abadie, A. , Diamond, A. and Hainmueller, J. (2010) Synthetic control methods for comparative case studies: estimating the effect of California's tobacco control program. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 105(490), 493–505.
-
- Abouk, R. and Heydari, B . (2020) The Immediate Effect of COVID‐19 Policies on Social Distancing Behavior in the United States . Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3571421 [Accessed 10th October 2020]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abrevaya, J. and Mulligan, K. (2011) Effectiveness of state‐level vaccination mandates: evidence from the varicella vaccine. Journal of Health Economics, 30(5), 966–976. - PubMed
-
- Ahammer, A. , Halla, M. and Lackner, M. (2020) Mass gatherings contributed to early COVID‐19 mortality: evidence from US sports . Economics Working Papers 2020‐13. Department of Economics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria.
-
- Ainslie, D. (2020) City of Sturgis Information Publication. Vol 12, Issue 4, April 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
