The Relationship Between Serum Cytokine Levels and the Degree of Psychosis and Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Methamphetamine-Associated Psychosis in Chinese Patients
- PMID: 33362607
- PMCID: PMC7759545
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.594766
The Relationship Between Serum Cytokine Levels and the Degree of Psychosis and Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Methamphetamine-Associated Psychosis in Chinese Patients
Abstract
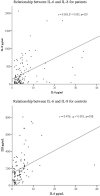
Background: Cytokine levels can be changed in methamphetamine (METH) use disorders (MUDs) and primary psychosis. The present study assessed serum levels of some kinds of interleukins (ILs) in METH-associated psychosis (MAP) and their relationships with psychotic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction. Methods: Serum IL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 levels were examined by chemiluminescence assays in MAP patients (n = 119) and healthy controls (n = 108). The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) were administered. Results: Serum levels of IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly increased in MAP patients (all p < 0.05). There was a negative relationship between IL-2R levels and PANSS positive (P) subscale scores (r = -0.193, p = 0.035). IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 levels were all negatively correlated with the naming, delayed recall and orientation subscores on the MOCA (r = -0.209, p = 0.022; r = -0.245, p = 0.007; r = -0.505, p < 0.001, respectively). Conclusions: Our results indicate that immune disturbances are related to MAP and that IL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 are associated with the severity of psychotic symptoms and cognitive function impairment.
Keywords: addiction; cognitive; methamphetamine; psychosis; serum cytokine.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Zhao, Liu, Xie, Zhou, Deng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- UNODC World Drug Report. Vienna, NY: United Nations Office of Drugs on Crime; (2018).
-
- Chinese National Narcotics Control Commission Annual Report on Drug Control in China. Zurich: (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources