Phosphoglucoisomerase Is an Important Regulatory Enzyme in Partitioning Carbon out of the Calvin-Benson Cycle
- PMID: 33362810
- PMCID: PMC7758399
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.580726
Phosphoglucoisomerase Is an Important Regulatory Enzyme in Partitioning Carbon out of the Calvin-Benson Cycle
Abstract
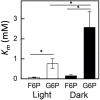
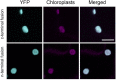
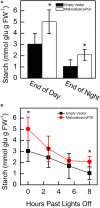
Phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) isomerizes fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) and glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) in starch and sucrose biosynthesis. Both plastidic and cytosolic isoforms are found in plant leaves. Using recombinant enzymes and isolated chloroplasts, we have characterized the plastidic and cytosolic isoforms of PGI. We have found that the Arabidopsis plastidic PGI K m for G6P is three-fold greater compared to that for F6P and that erythrose 4-phosphate is a key regulator of PGI activity. Additionally, the K m of spinach plastidic PGI can be dynamically regulated in the dark compared to the light and increases by 200% in the dark. We also found that targeting Arabidopsis cytosolic PGI into plastids of Nicotiana tabacum disrupts starch accumulation and degradation. Our results, in combination with the observation that plastidic PGI is not in equilibrium, indicates that PGI is an important regulatory enzyme that restricts flow and acts as a one-way valve preventing backflow of G6P into the Calvin-Benson cycle. We propose the PGI may be manipulated to improve flow of carbon to desired targets of biotechnology.
Keywords: Calvin-Benson cycle; carbon partitioning; erythrose 4-phosphate; phosphoglucoisomerase; starch.
Copyright © 2020 Preiser, Banerjee, Weise, Renna, Brandizzi and Sharkey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abiri R., Valdiani A., Maziah M., Azmi Shaharuddin N., Sahebi M., Norhana Balia Yusof Z., et al. (2016). A critical review of the concept of transgenic plants: insights into pharmaceutical biotechnology and molecular farming. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 18 21–42. - PubMed
-
- Alberty R. A. (1953). The relationship between Michaelis constants, maximum velocities and the equilibrium constant for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75 1928–1932. 10.1021/ja01104a045 - DOI
-
- Ausich R. L. (2009). Commercial opportunities for carotenoid production by biotechnology. Pure Appl. Chem. 69 2169–2173. 10.1351/pac199769102169 - DOI
-
- Backhausen J. E., Jöstingmeyer P., Scheibe R. (1997). Competitive inhibition of spinach leaf phosphoglucose isomerase isoenzymes by erythrose 4-phosphate. Plant Sci. 130 121–131. 10.1016/s0168-9452(97)00208-202 - DOI
-
- Bahaji A., Sánchez-López ÁM., De Diego N., Muñoz F. J., Baroja-Fernández E., Li J., et al. (2015). Plastidic phosphoglucose isomerase is an important determinant of starch accumulation in mesophyll cells, growth, photosynthetic capacity, and biosynthesis of plastidic cytokinins in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 10:e0119641. 10.1371/journal.pone.0119641 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

