State of the Field in Multi-Omics Research: From Computational Needs to Data Mining and Sharing
- PMID: 33362867
- PMCID: PMC7758509
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.610798
State of the Field in Multi-Omics Research: From Computational Needs to Data Mining and Sharing
Abstract
Multi-omics, variously called integrated omics, pan-omics, and trans-omics, aims to combine two or more omics data sets to aid in data analysis, visualization and interpretation to determine the mechanism of a biological process. Multi-omics efforts have taken center stage in biomedical research leading to the development of new insights into biological events and processes. However, the mushrooming of a myriad of tools, datasets, and approaches tends to inundate the literature and overwhelm researchers new to the field. The aims of this review are to provide an overview of the current state of the field, inform on available reliable resources, discuss the application of statistics and machine/deep learning in multi-omics analyses, discuss findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable (FAIR) research, and point to best practices in benchmarking. Thus, we provide guidance to interested users of the domain by addressing challenges of the underlying biology, giving an overview of the available toolset, addressing common pitfalls, and acknowledging current methods' limitations. We conclude with practical advice and recommendations on software engineering and reproducibility practices to share a comprehensive awareness with new researchers in multi-omics for end-to-end workflow.
Keywords: FAIR; benchmarking; data heterogeneity; integrated omics; machine learning; multi-omics; reproducibility; visualization.
Copyright © 2020 Krassowski, Das, Sahu and Misra.
Conflict of interest statement
VD currently works as a Post-Doctoral Researcher in Novo Nordisk Research Center Seattle, Inc. He did not receive any funding for this work. BBM works as a Computational Biologist in Enveda Therapeutics and did not receive any funding for this work. SS has no conflicts of interest. MK has no financial conflicts of interest, but he contributed to two of the discussed projects: rpy2 and Jupyter.
Figures


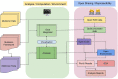

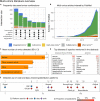
References
-
- Amodio M., Krishnaswamy S. (2018). “MAGAN: aligning biological manifolds,” in 35th International Conference on Machine Learning ICML 2018, Vol. 1 Stockholm, 327–335.
-
- Amstutz P., Chapman B., Chilton J., Heuer M., Stojanovic E. (2016). Common Workflow Language, v1.0 Common Workflow Language (CWL) Command Line Tool Description, v1.0. 10.6084/m9.figshare.3115156.v2 - DOI
-
- BACnet Stack (2020). BACnet Stack. Available online at: https://github.com/bacnet-stack (accessed August 3, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

