Polymeric Iodophors: Preparation, Properties, and Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 33362938
- PMCID: PMC7749746
- DOI: 10.1134/S2079978020010033
Polymeric Iodophors: Preparation, Properties, and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
The review summarizes the data on the main chemical and physiological properties of iodine and its capability of complexation with natural and synthetic polymers. Iodine is the best known antiseptic used to prevent and treat microbial infections. Its unique capability of complexation with certain polymers opens wide opportunities for targeted and prolonged delivery to target organs. Polymeric complexes with iodine have another color, other morphology, a higher electrical conductivity, and higher biological activity as compared with initial polymers. The formation of and ions is associated with iodine-polymer complexation. Iodine-containing biocompatible adhesive controlled-release formulations are designed as part of research into iodine-polymer complexes. The field is promising in terms of treating certain diseases because tolerance to iodine compounds does not usually develop in microbial cells.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; antiseptics; biological activity; iodine–polymer complexes; iodophors.
© Pleiades Publishing, Ltd. 2020, ISSN 2079-9780, Review Journal of Chemistry, 2020, Vol. 10, No. 1–2, pp. 40–57. © Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2020.
Figures


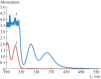







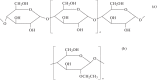
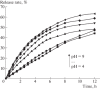




References
-
- Boddie, R. and Nickerson, S.C., J. Dairy Sci., 2016, vol. 80, no. 8, p. 1846. - PubMed
-
- Kaiho T. Iodine Chemistry and Applications. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
